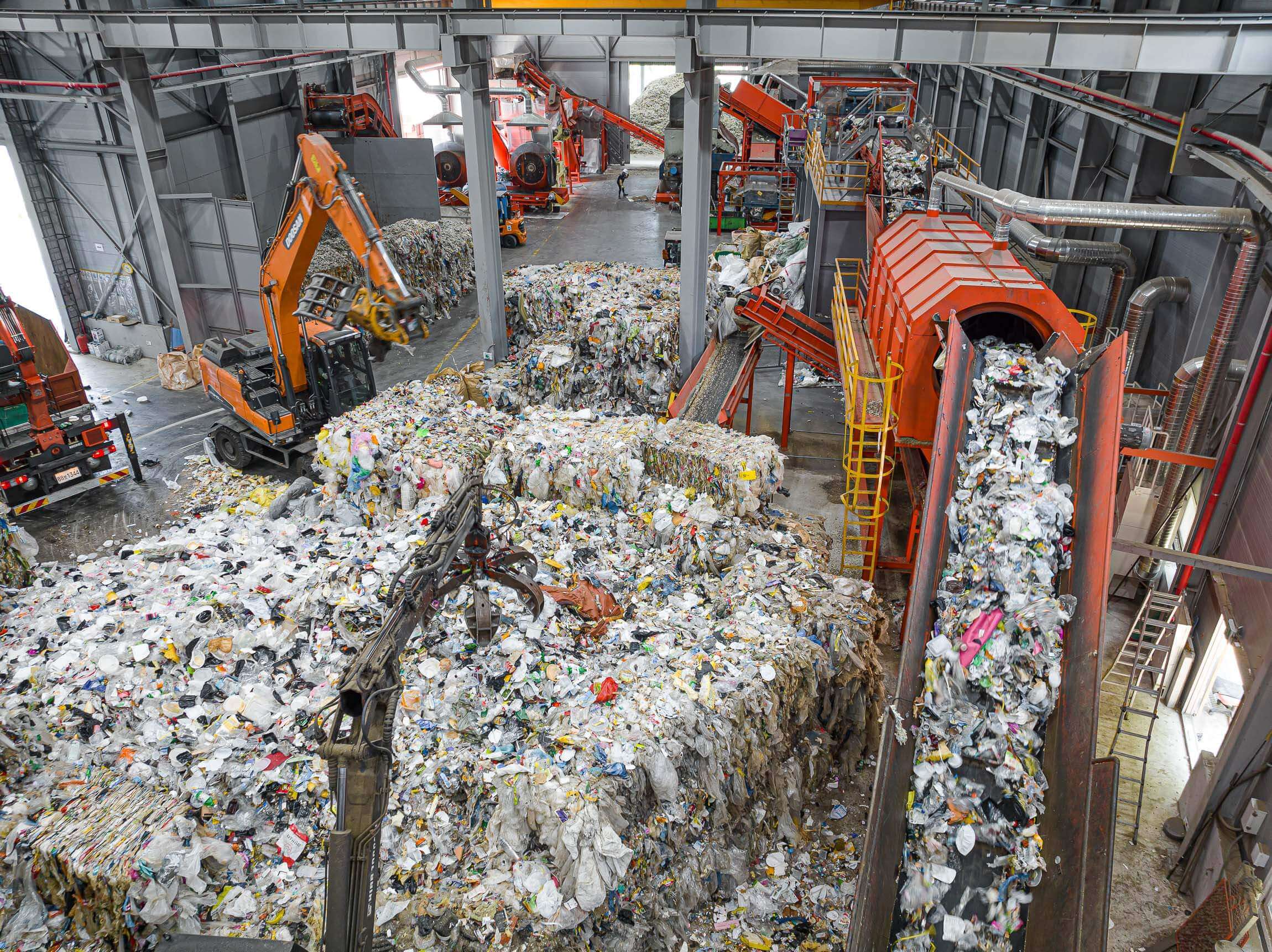
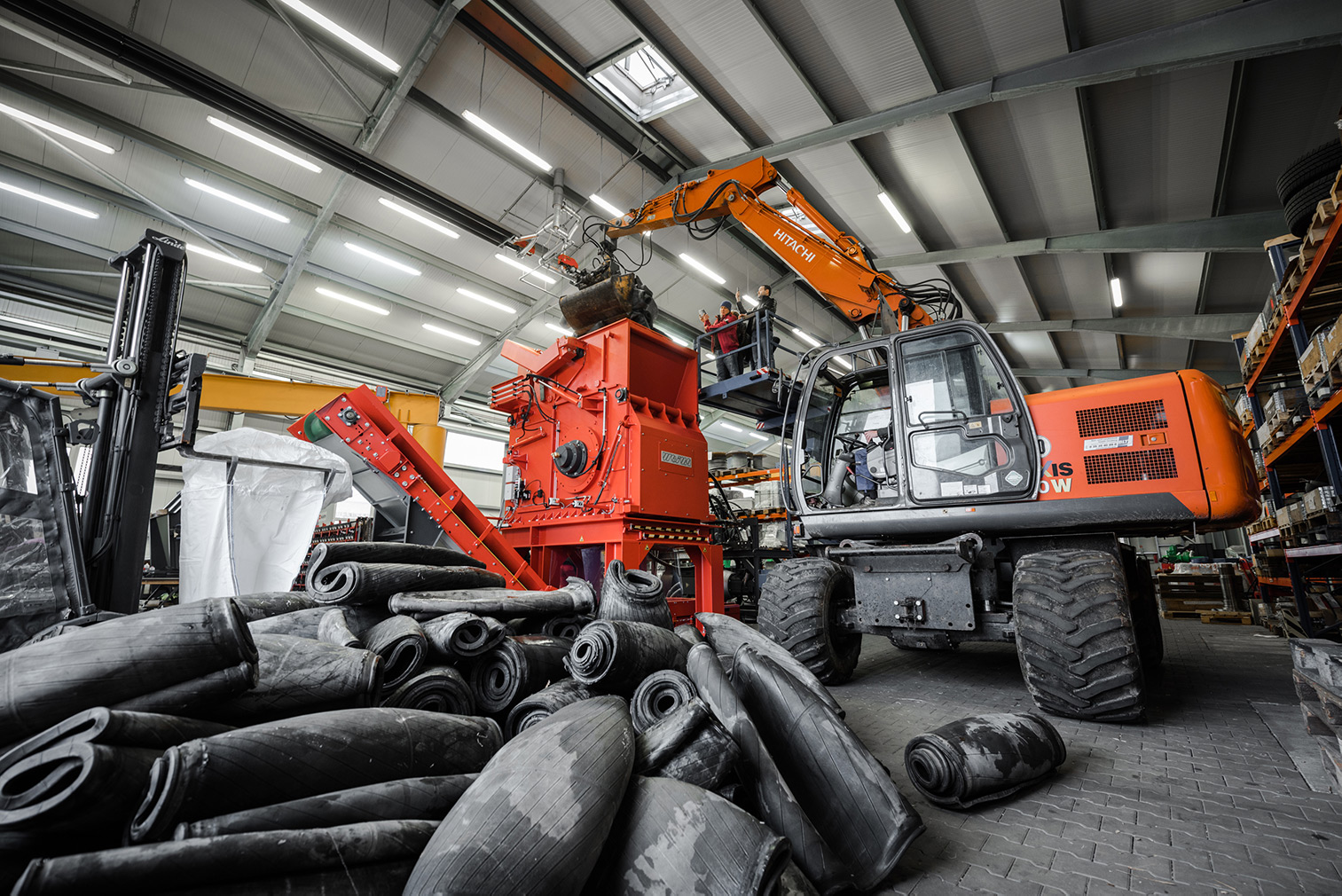
Waste Shredding and Secondary Fuel Production for Waste-to-Energy
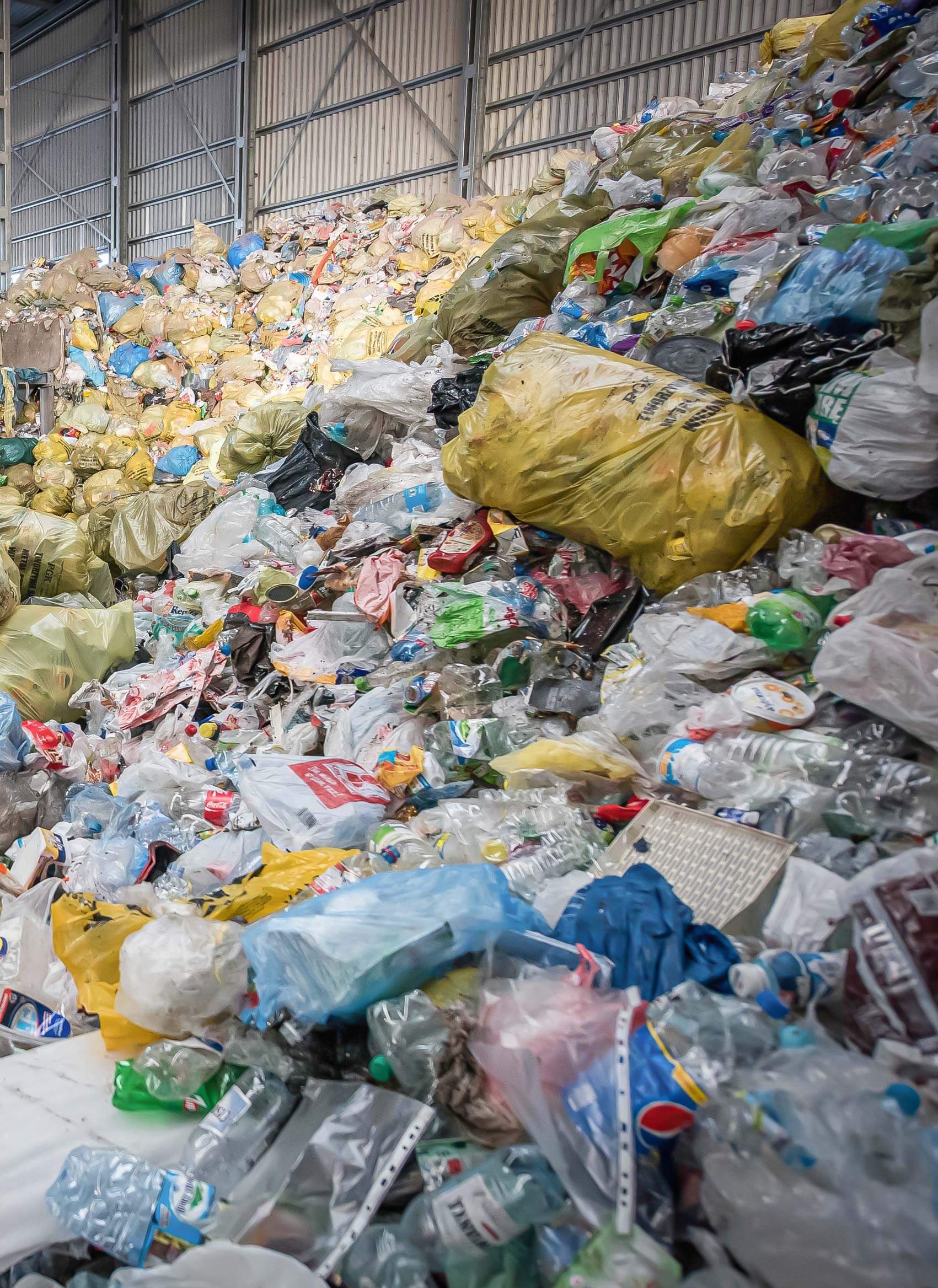
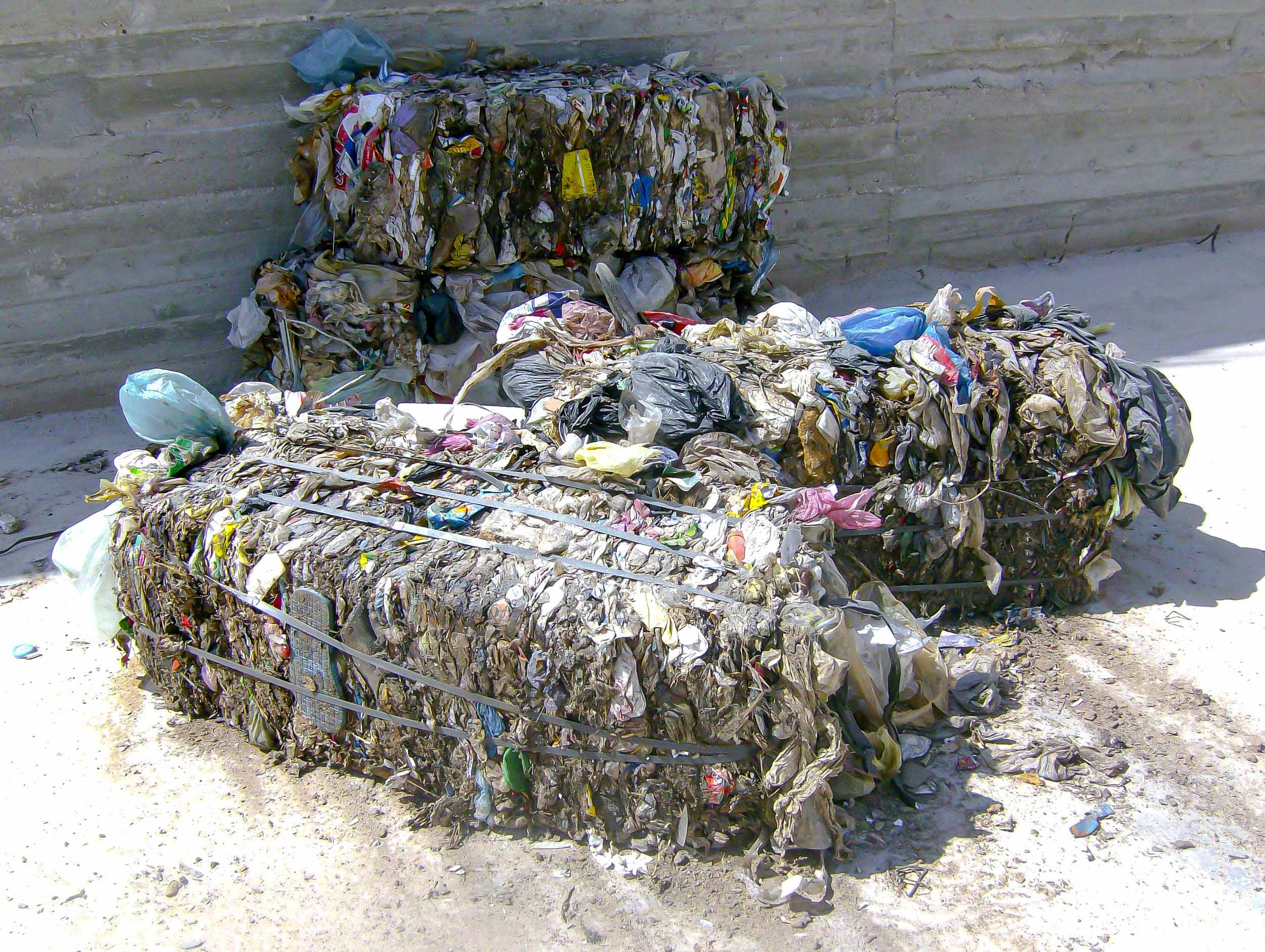
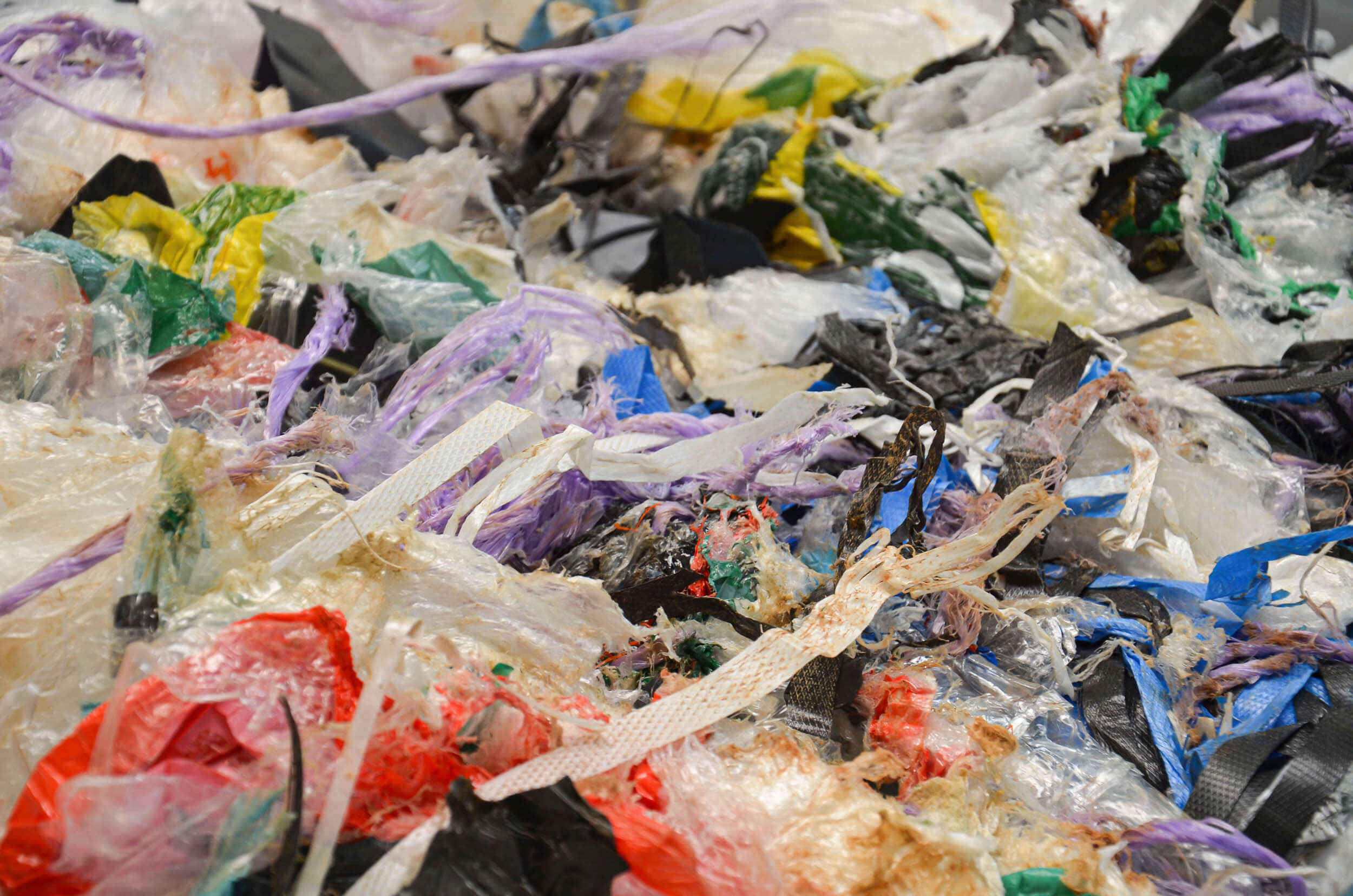
Waste is a valuable material. Whether commercial waste, bulky or household waste, production rejects, rejects and paper, municipal waste, wood residues and carpet materials: WEIMA ensures high-throughput waste shredding and an optimal result in the extraction of valuable secondary fuels (RDF).
Robustly designed pre-shredders and shredders are used worldwide as a stand-alone solution or as part of a multi-stage waste treatment plant. The output material from different material fractions is ideally suited for the production of high-calorific alternative fuels (RDF). These are in particularly high demand for the production of energy for the cement industry.
Waste Shredding and Secondary Fuel Production for Waste-to-Energy Waste Shredding and Secondary Fuel Production for Waste-to-Energy Waste Shredding and Secondary Fuel Production for Waste-to-Energy
These shredders are currently particularly popular.
Learn more about waste processing and production of refuse derived fuel (RDF) and solid recovered fuel (SRF)
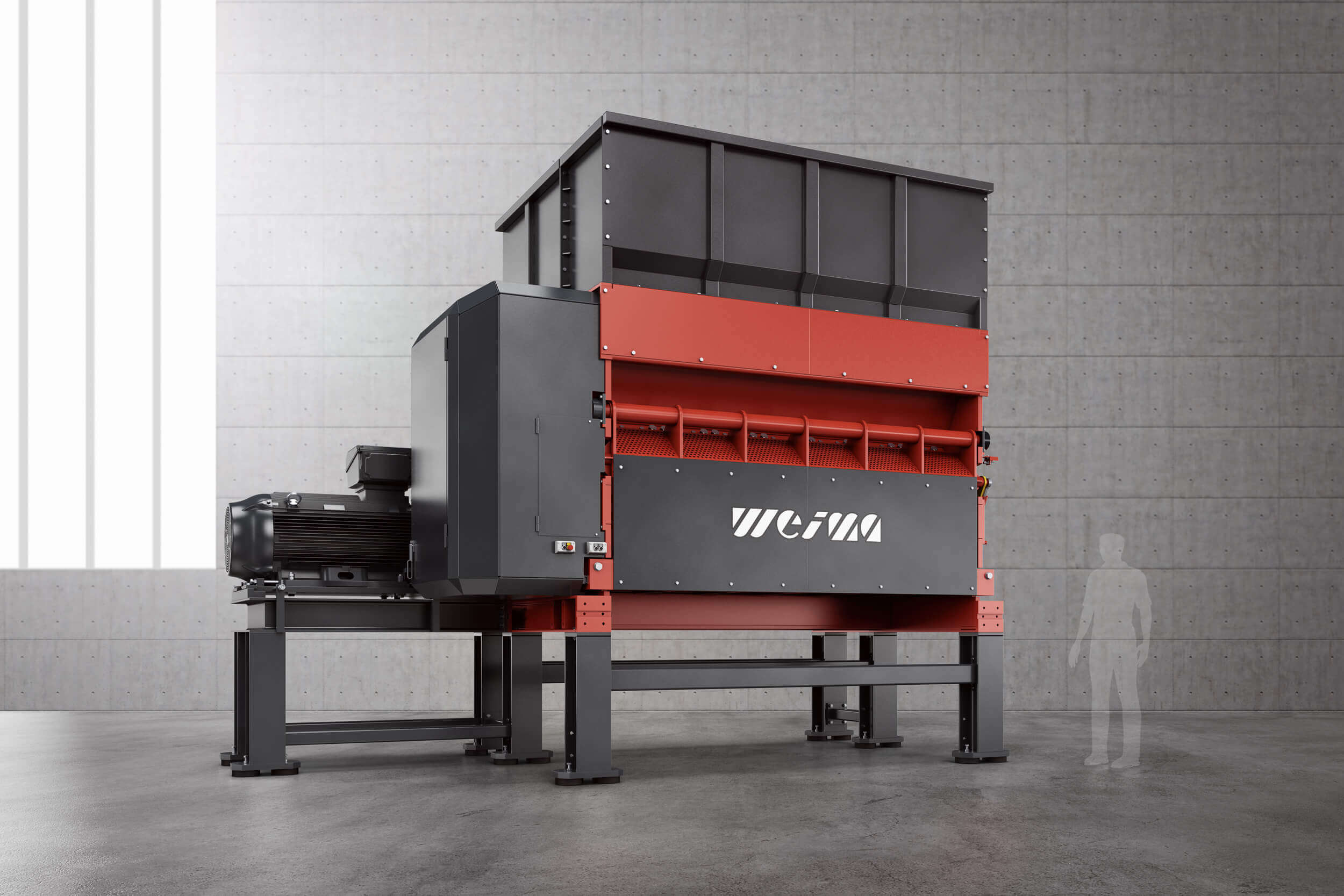
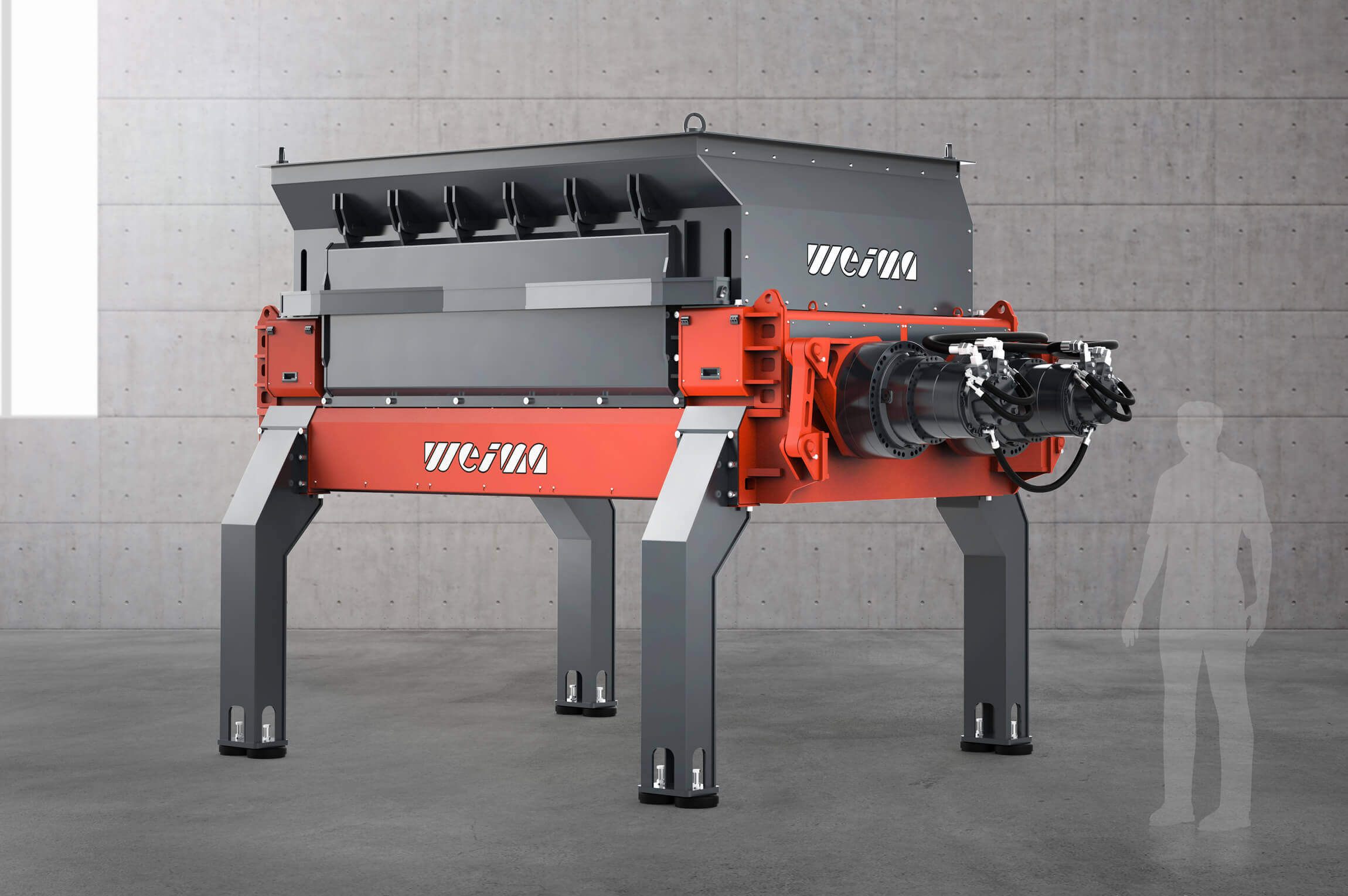
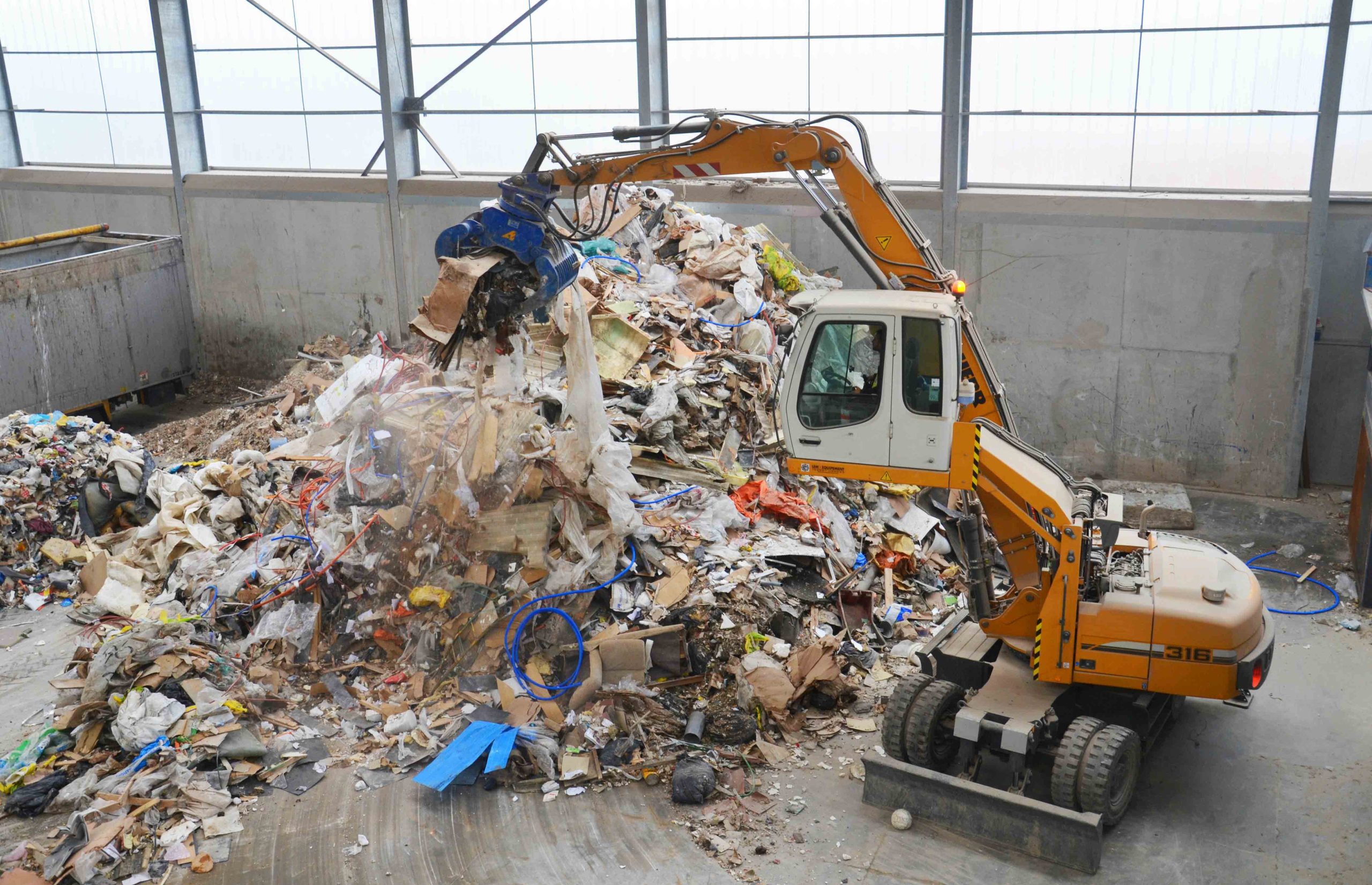
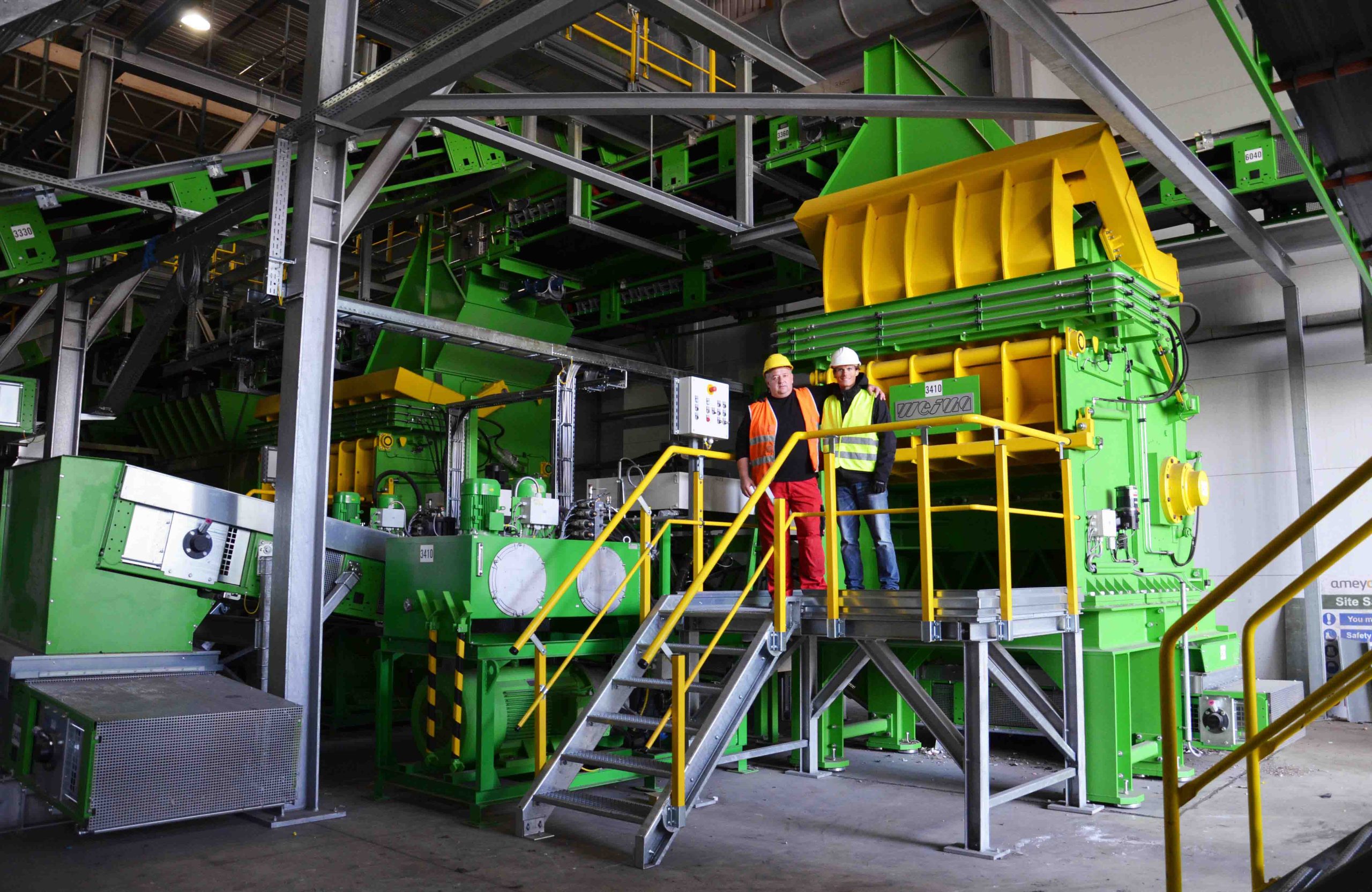
Shredder for pre-shredding and secondary shredding of waste
"Ain't no waste mountain high enough..."
With our shredding solutions we would like to contribute to the fact that waste that is no longer usable, but nevertheless valuable, does not find its way to the landfill site, but is used for energy generation. In doing so, the use of fossil fuels is further reduced, which protects the environment and is usually more economical.
"40 tons! This is the throughput a WEIMA waste shredder achieves per hour in the production of high-quality substitute fuel."
Erik Hagen
Business Development | Waste at WEIMA
Customer applications and examples
From the secondary fuel industry and waste disposal
Fiery passion for substitute fuel
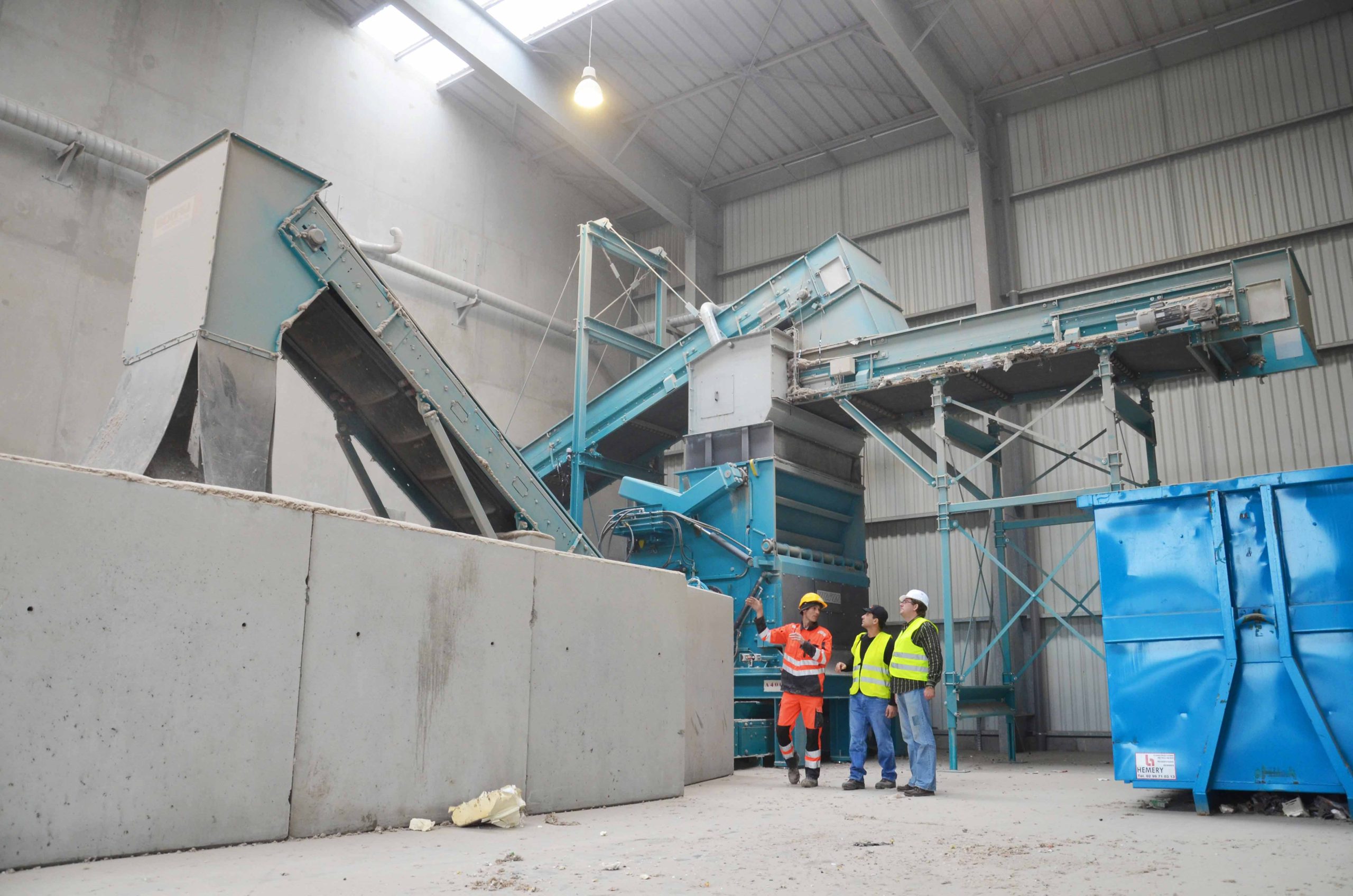
The shredding of material streams is the cornerstone of any recycling process. Industrial shredders are used here. With the PowerLine, PreCut and FineCut Shredders, WEIMA demonstrates the potential of single and multi-stage processing of waste.
Stand-alone operation or integration into a production line – tap into the waste-to-energy potential
Depending on your requirements, we can supply you with the right shredder for your recycling task. If required, WEIMA also offers a multi-stage system solution in the form of a plant. We are assisted in this by an extensive supplier and service network that we have built up over the last decades. This includes specialists in the areas of conveyor technology, sorting, separation, screening technology, washing technology, metal detection, extrusion, heating construction and granulation. As a joint project team, we have already mastered hundreds of major tasks all over the world.
Inquire about a waste shredder today
Request a quote
Use of alternative fuels in cement production
The cement industry has a very high demand for energy. This can increasingly be covered by substitute fuels. The focus is on the combustion of alternative fuels in calciners, pre-burners and kilns. In order to reduce energy costs, cement manufacturers are placing more and more emphasis on increasing the proportion of alternative fuels in energy production. Compared to classic materials, the thermal utilization of these fuels has better physical burning properties and better burnout in the kiln. In general, the better the secondary fuel used, the more efficient the production of high-quality clinker.
Waste shredders for co-processing
The production of cement requires enormous amounts of energy. To cover this sustainably, the use of secondary fuels is crucial. But co-processing is more than simply burning waste to generate energy.
Definition: What is co-processing?
The term co-processing describes a globally recognized technology used in energy-intensive industries (EII) such as cement production to recycle waste and industrial by-products for energy and materials. The mineral components in the waste replace primary raw materials (e.g. limestone) in the cement kiln, while the combustible materials provide the necessary energy for the production of clinker. No residual materials are produced in the process, and highly toxic wastes are also destroyed. Co-processing thus makes it possible to avoid landfilling and incineration of wastes such as sewage sludge, solvents, plastics from industry or mineral wastes.
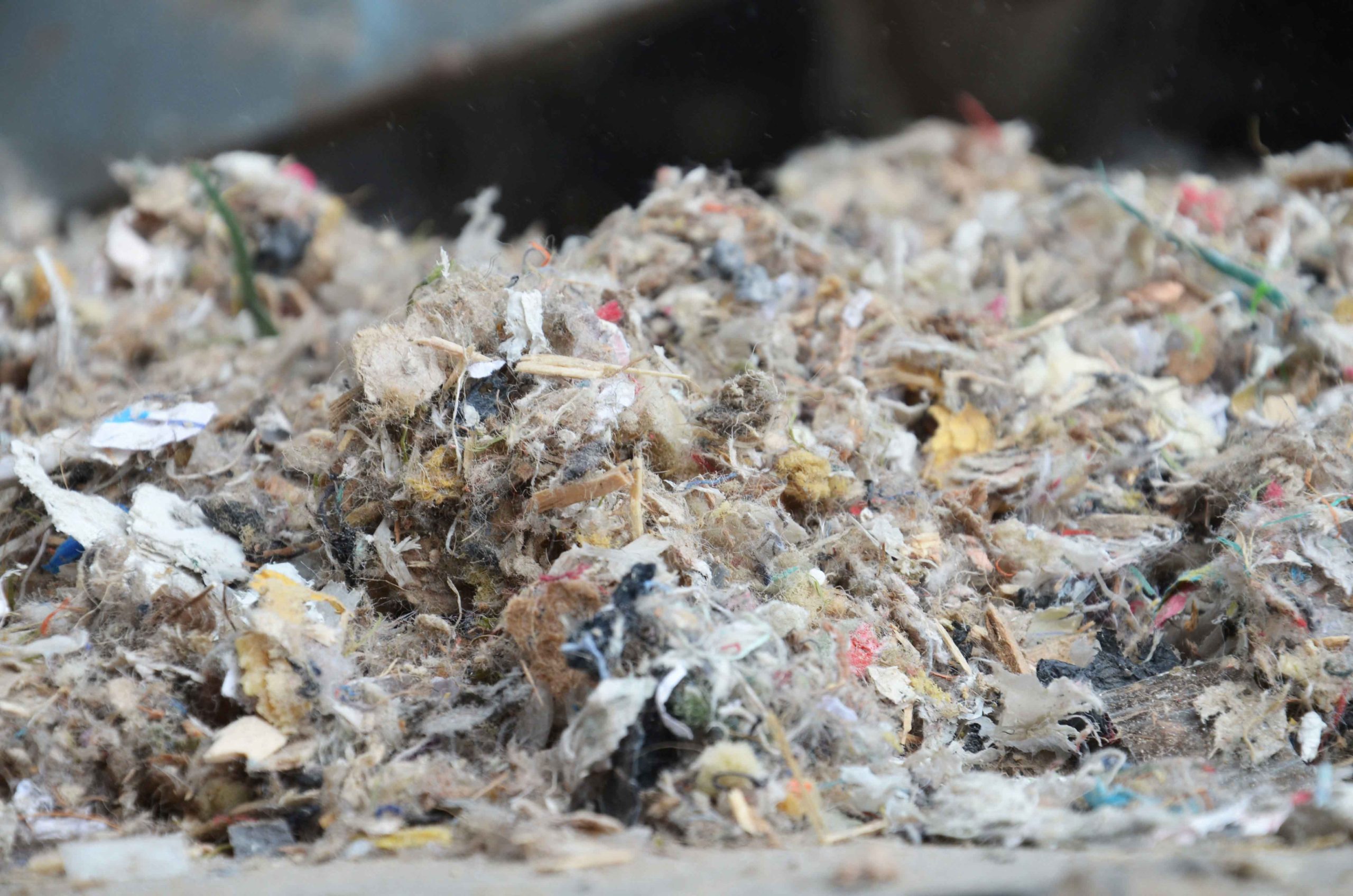

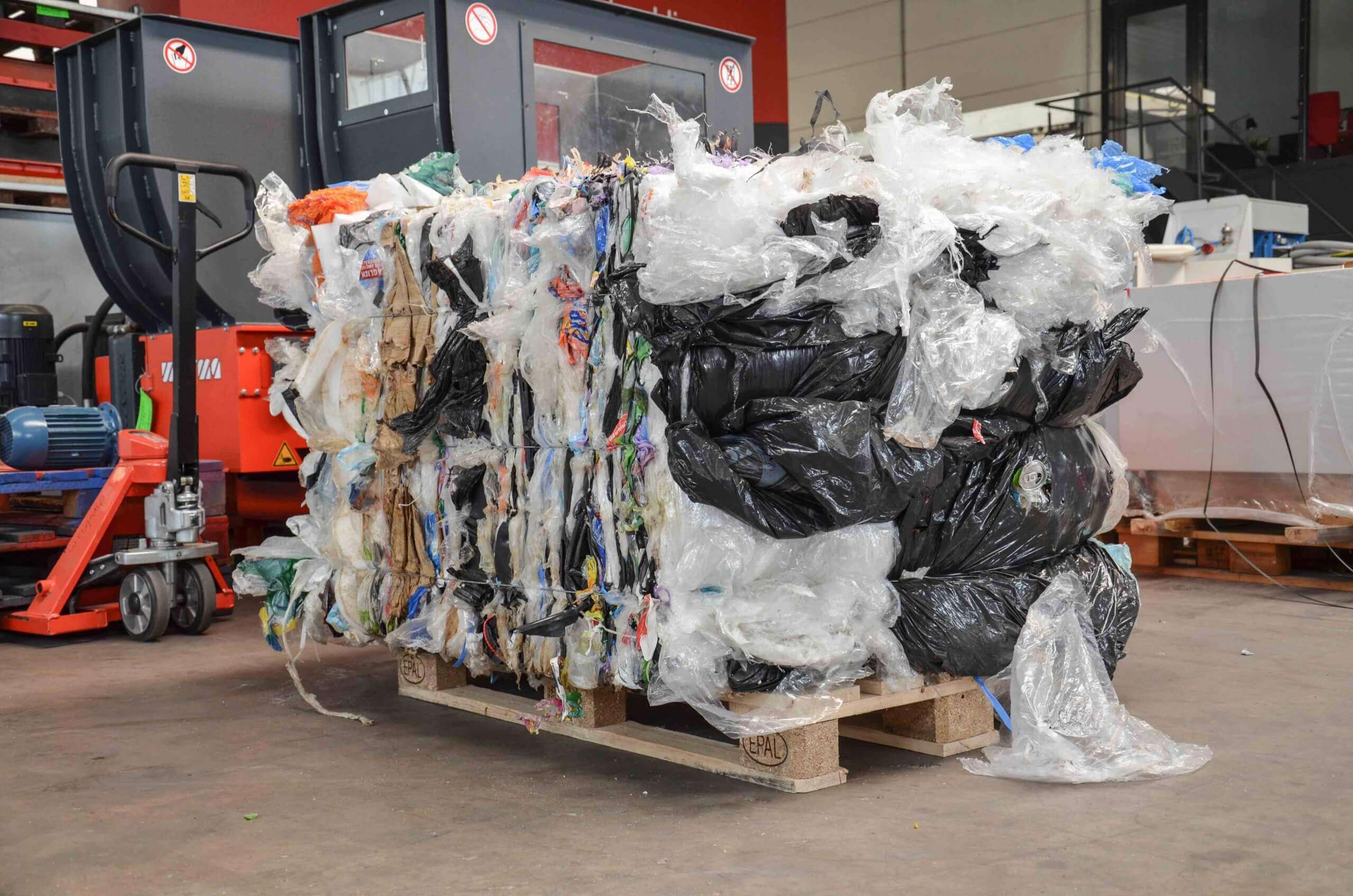
RDF substitute fuel
Advantages of Co-Processing
Co-processing in the context of cement production has many advantages: The extremely high temperatures and long residence time in the kiln completely destroy even hazardous and toxic waste. No residual materials are produced that have to be further recycled or landfilled. The use of co-processing technology also avoids the need to use fossil fuels and consequently reduces greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, cement manufacturers can massively reduce their energy costs thanks to secondary fuels from waste.

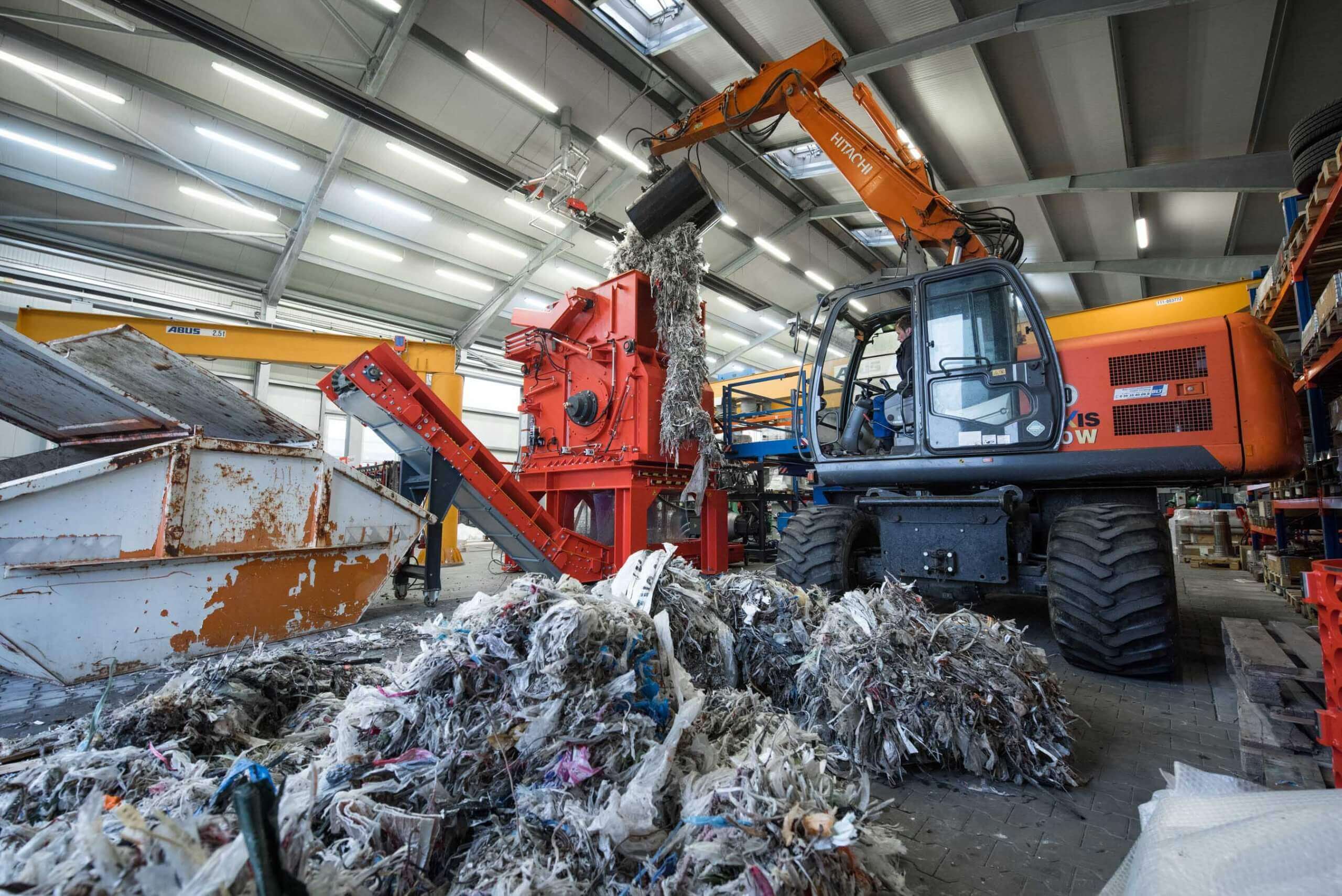
Shredder waste

Shredding of production waste
Pre-Processing with WEIMA shredders
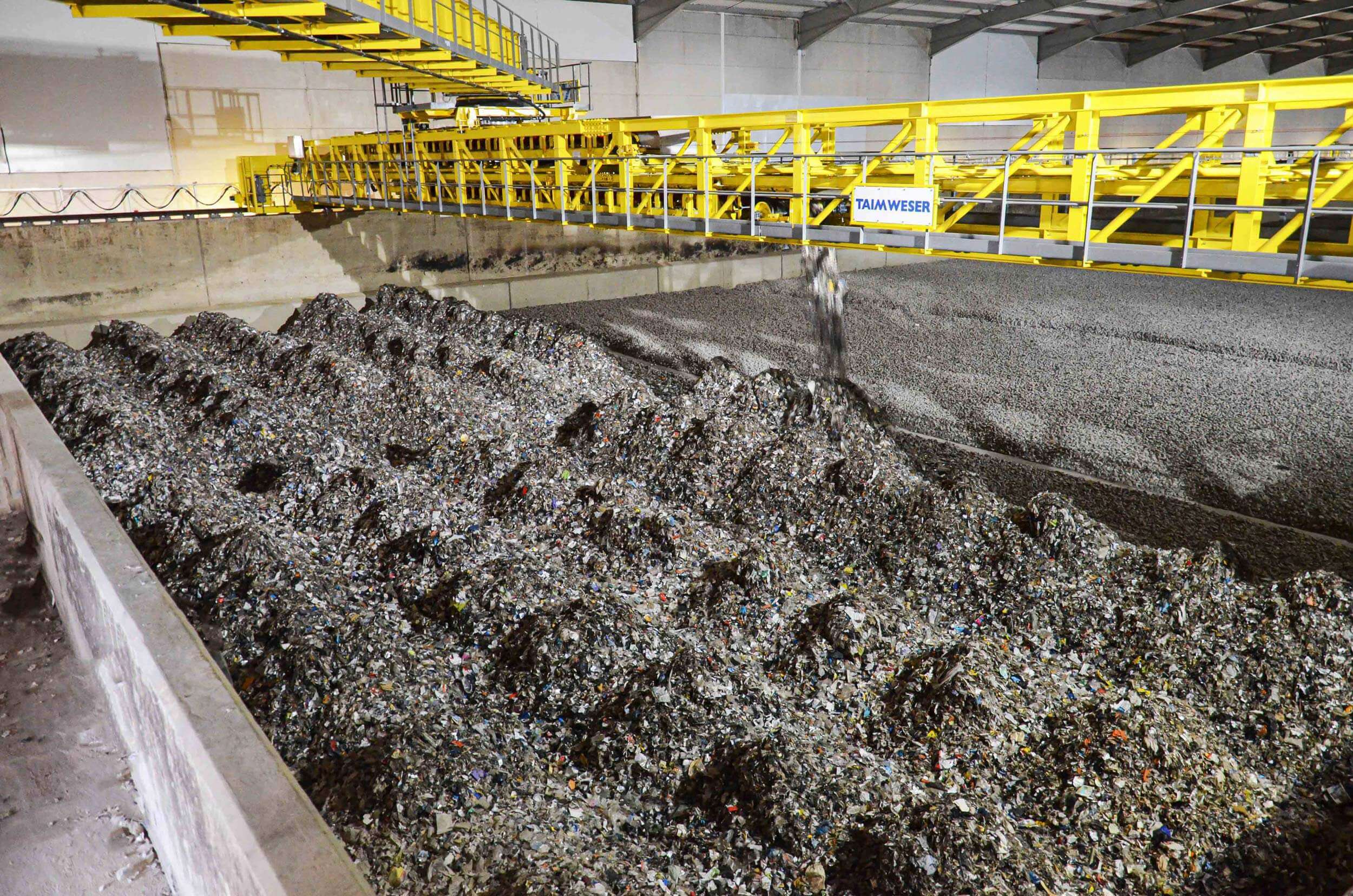
Generally, waste cannot directly processed in cement kilns, but must be prepared beforehand. The treatment process, also called pre-processing, includes the shredding, mixing and drying of waste. The use of WEIMA shredders in pre-processing enables consistently homogeneous particle sizes of the most demanding material. This guarantees a stable fuel that meets the technical requirements of cement production.
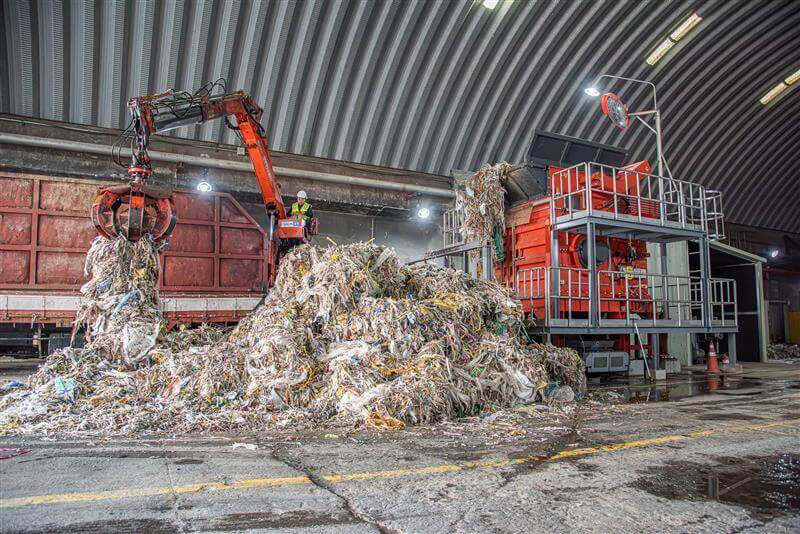
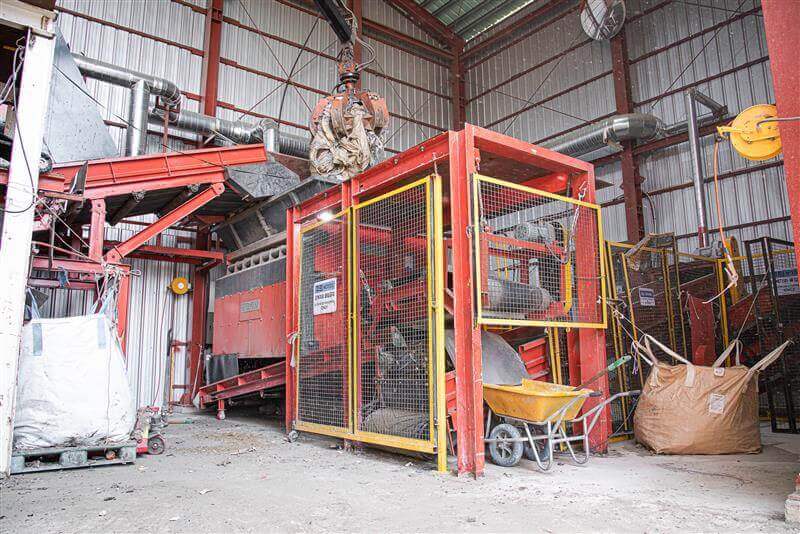
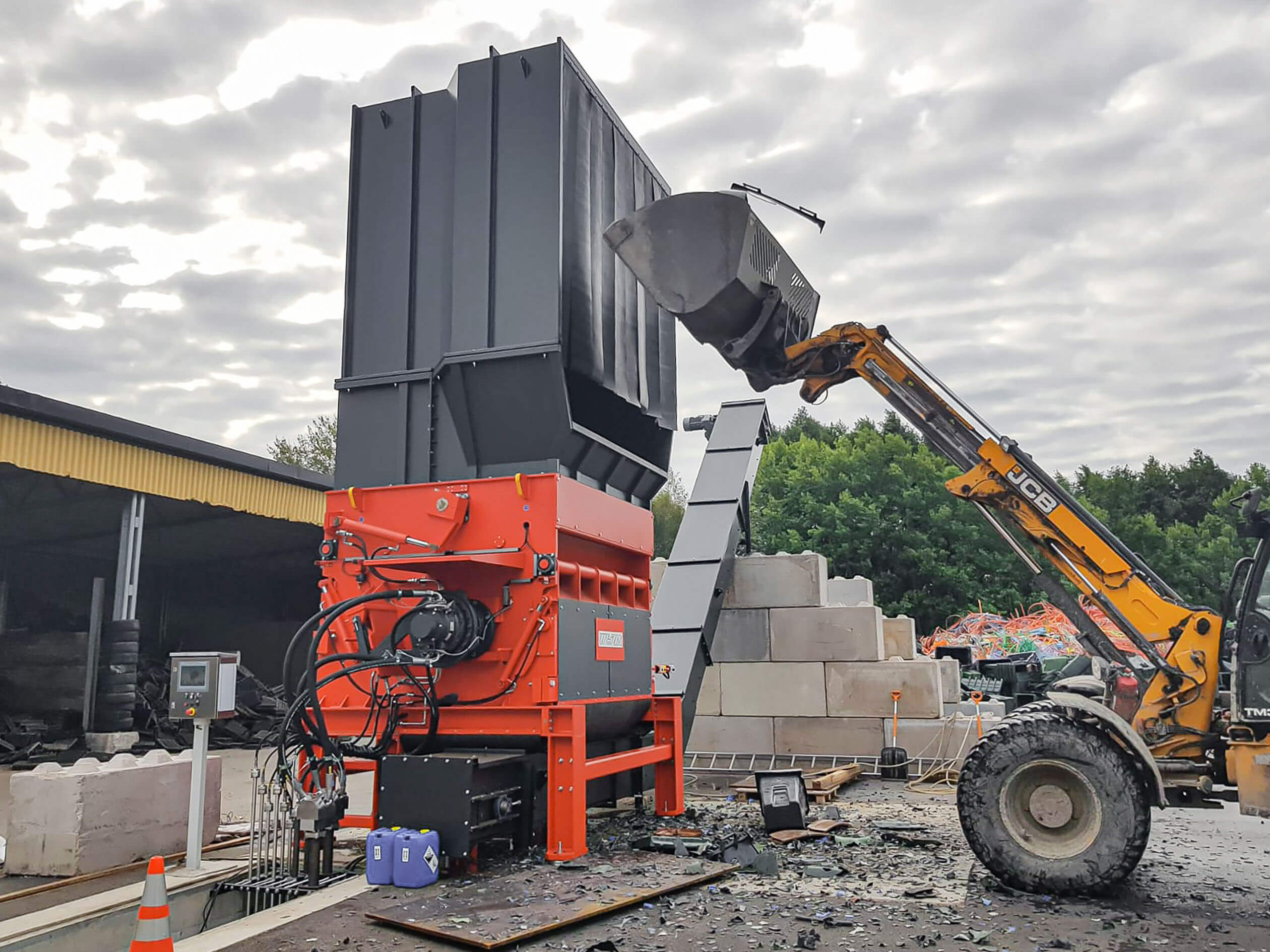
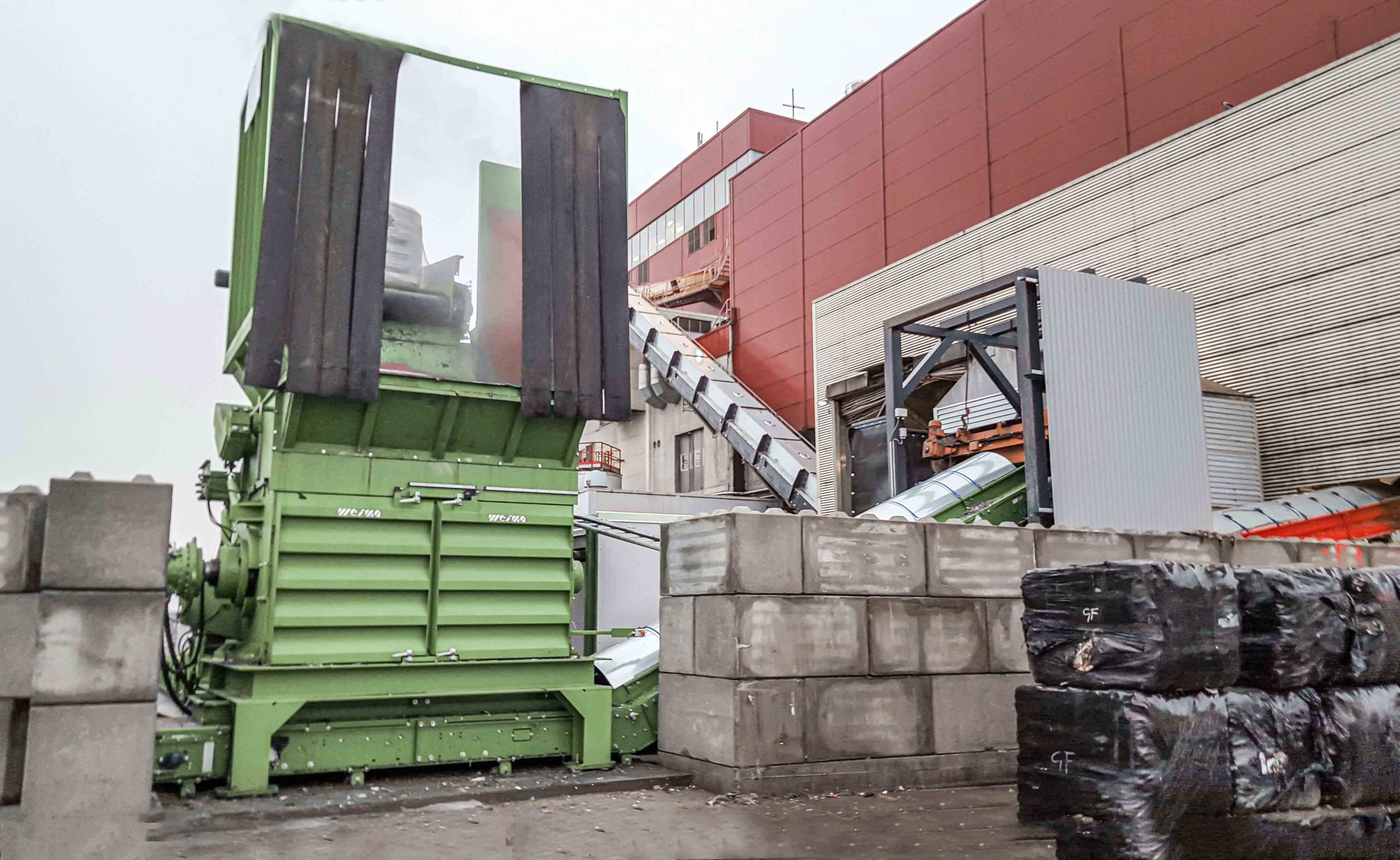
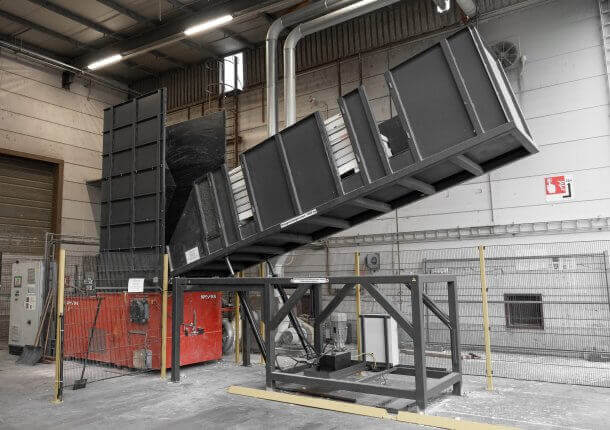
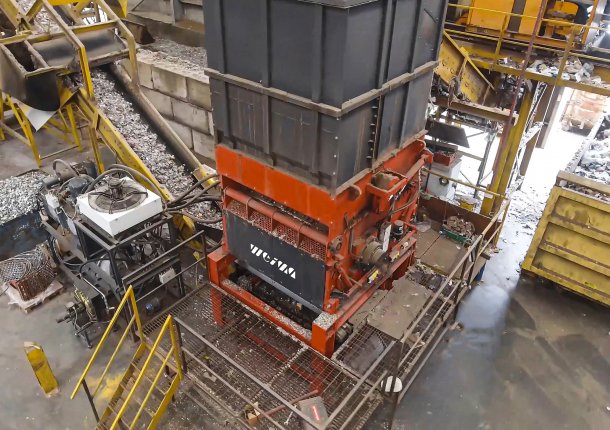
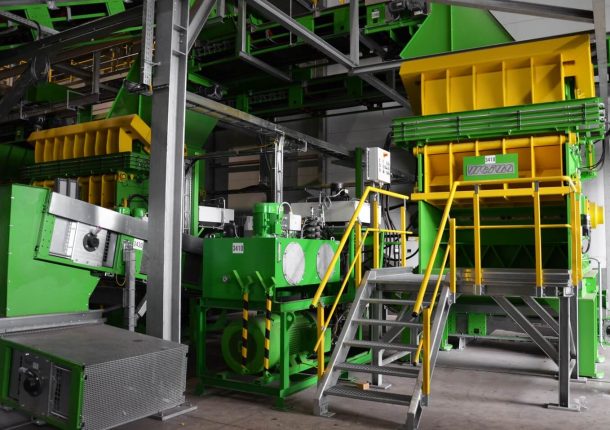
Industrial (C&I) and municipal waste (MSW) shredding with a WEIMA S7.30 lift-up shredder in Korea
A WEIMA S7.30 lift-up single-shaft shredder with a hydraulic drive by Hägglunds Bosch Rexroth shreds various kinds of waste for the production of RDF at Daewon Recycling in Gimje, South Korea.
You are interested in waste?
Here you can learn more about the most important basic terms:
Alternative fuel
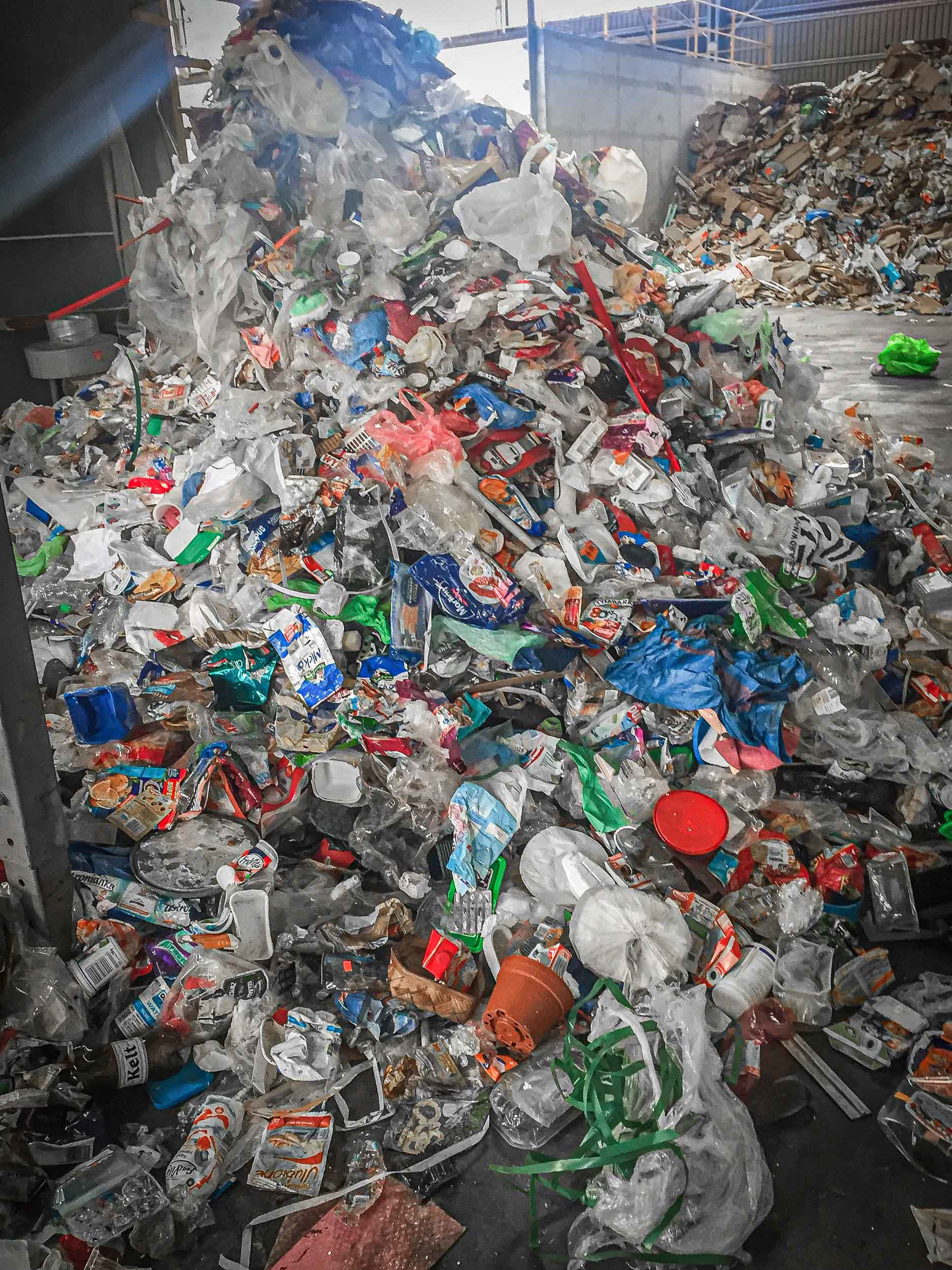
WEIMA waste shredders are ideally suited for the production of medium and high calorific RDF (refuse derived fuel). These are fuels that are obtained from household, industrial and municipal waste. The different quality requirements depend on the thermal process. The typical processing steps of the high-calorific fraction include pre-sorting, pre-shredding, air separation and metal separation. Sensory sorting and drying are also possible. In most cases substitute fuel is used together with conventional fuels, e.g. in cement, lime, coal and industrial power plants.
Mechanical-biological waste treatment (MBT)
Generally speaking, this is household waste, MSW or commercial waste similar to household waste. This is first collected by waste management companies and transported to a central location for waste treatment, disposal or recycling. Typically, household waste contains a high proportion of organic substances. After a coarse pre-sifting, it is shredded and then divided into different fractions by screening. The coarse fraction (foil, paper, hard plastics, wood, etc.) is mostly used as fuel in RDF power plants due to its high caloric value. The fine fraction (organic substances), on the other hand, is usually treated further biologically. Gases produced in this way can be used to generate energy.
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
Household or municipal waste is usually referred to as MSW, collected in bags or garbage cans and collected by municipal or private waste service providers. This does not include commercial or industrial waste. While the organic components can be composted or otherwise made biologically usable, the majority of municipal household waste serves as an alternative fuel for various energy-intensive industries.
Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF)
The production of SRF usually requires additional process steps, as higher quality requirements for its production have been defined at European level. The essential properties of a classification include the calorific value as well as the chlorine and mercury content. This results in five quality classes to be able to call processed waste Solid Recovered Fuel.
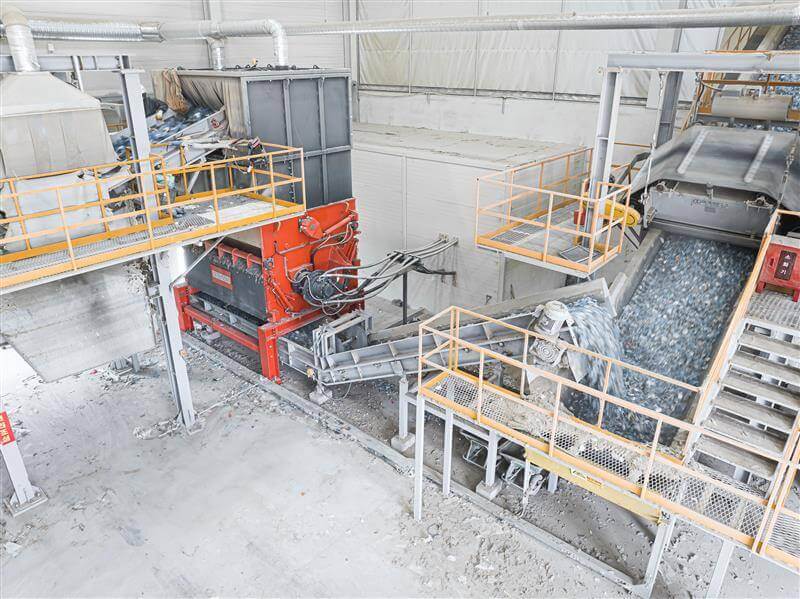
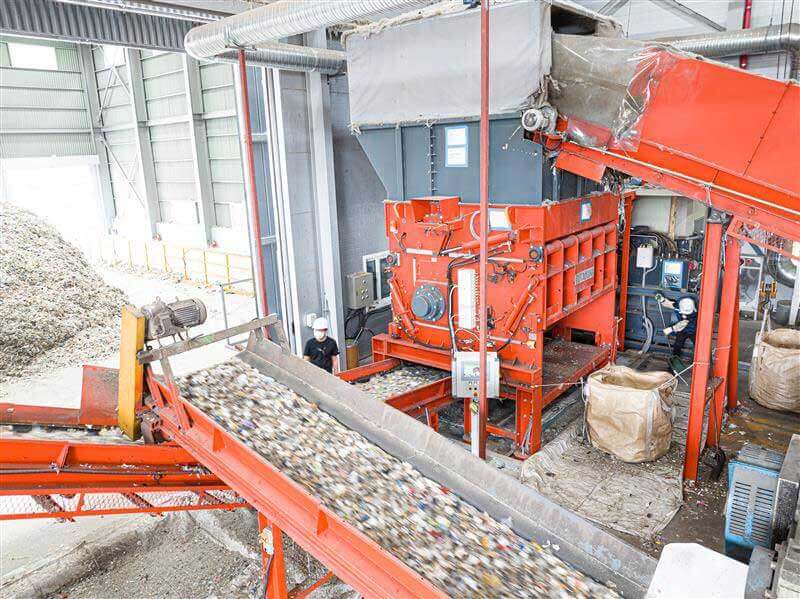
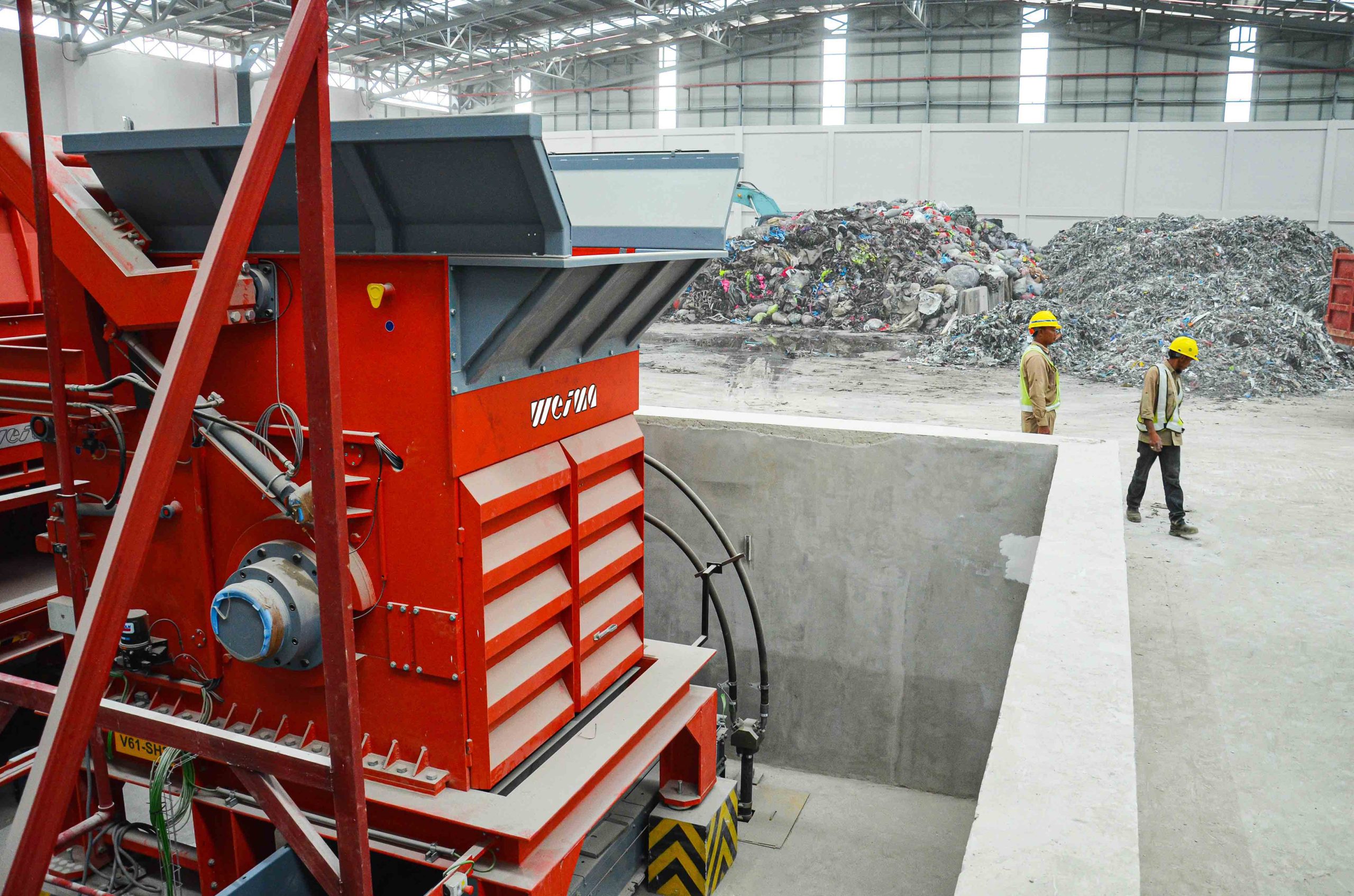
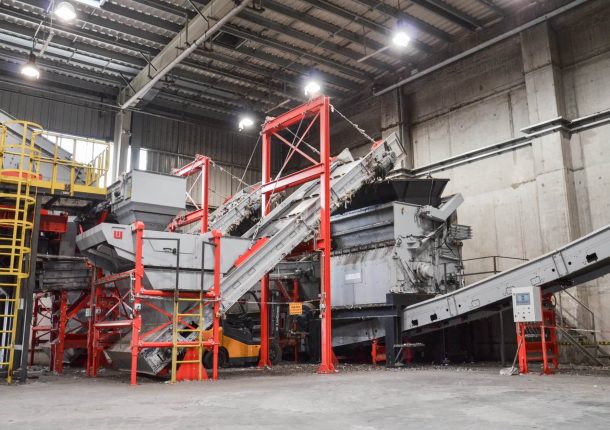
MSW waste shredders | WEIMA PreCut 2000 and PowerLine 2500 @Sunchang Energy
A WEIMA PreCut 2000 single-shaft shredder pre-shreds municipal solid waste for the production of refuse-derived fuels (RDF). Secondary shredding happens with a WEIMA PowerLine 2500 single-shaft shredder. Both shredders are equipped with a hydraulic drive by Hägglunds Bosch Rexroth.
May we present?
Your waste shredder trio
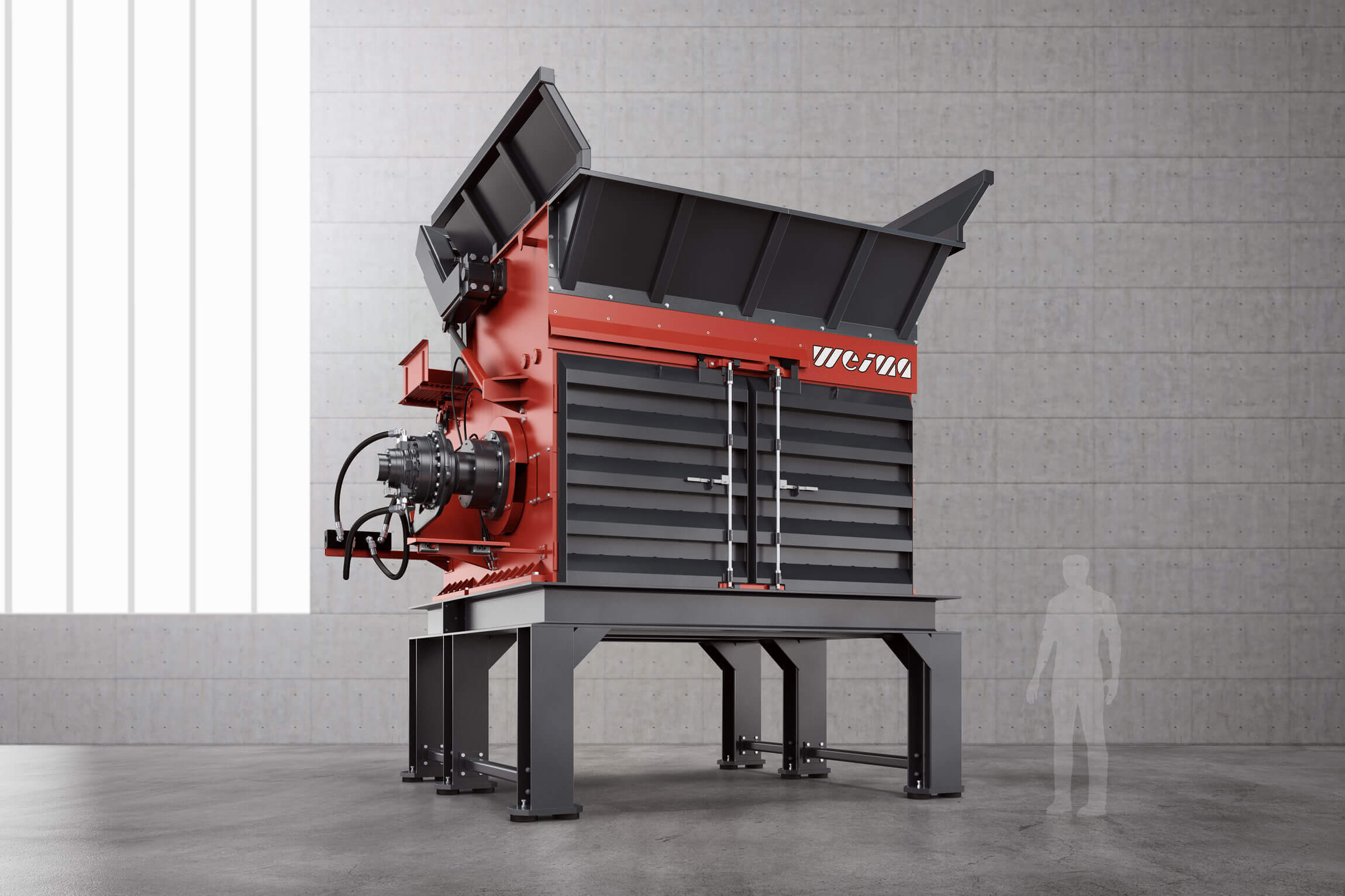
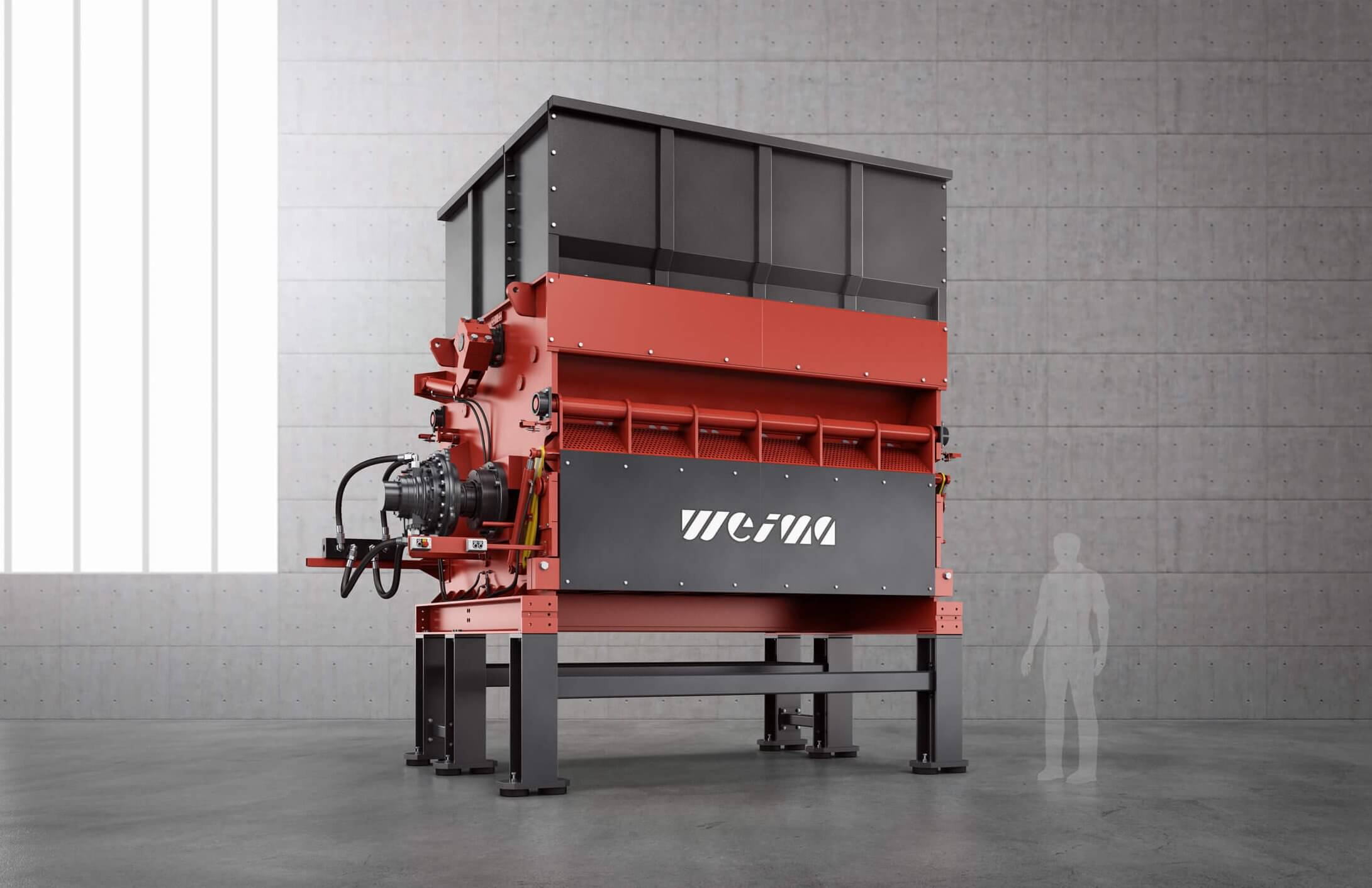
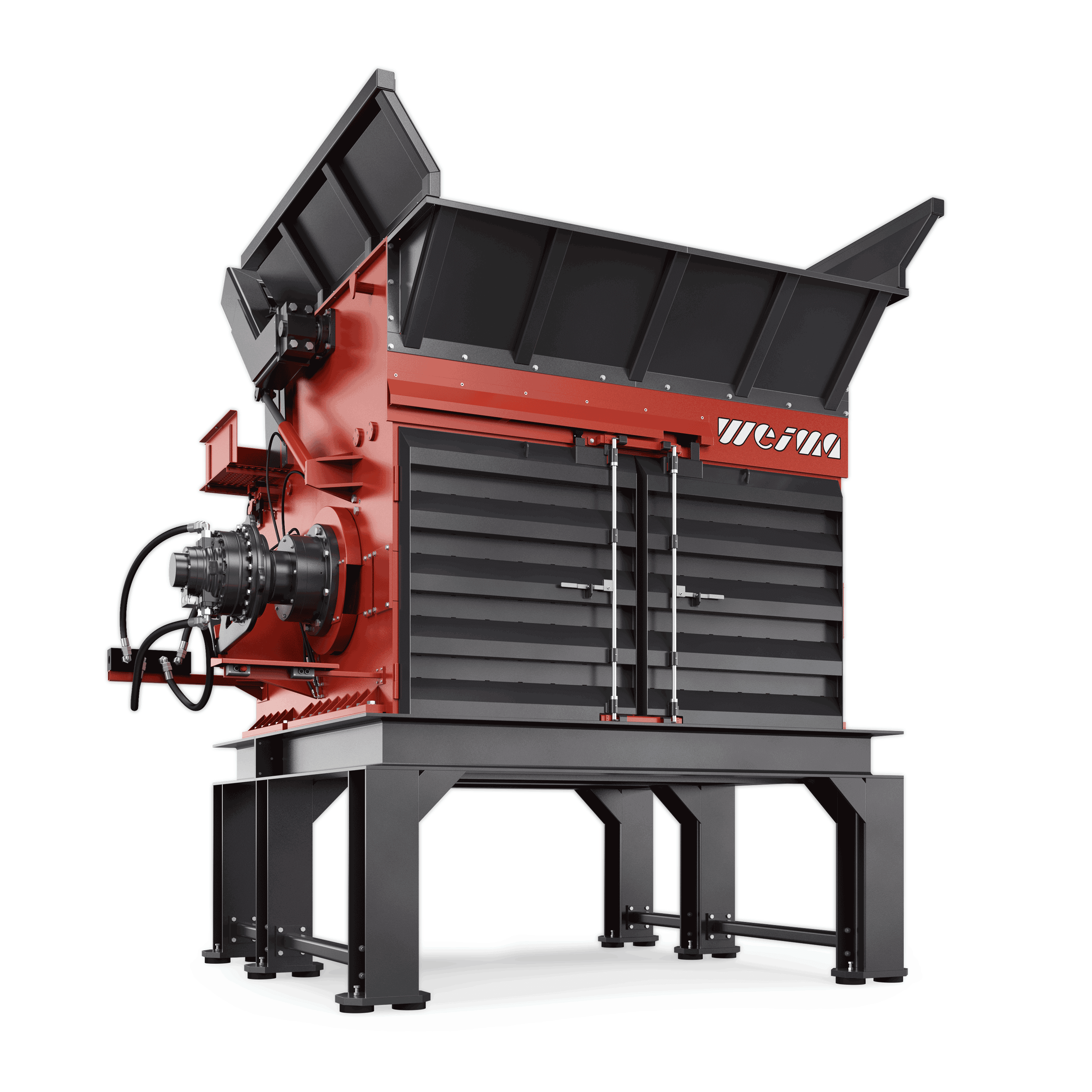
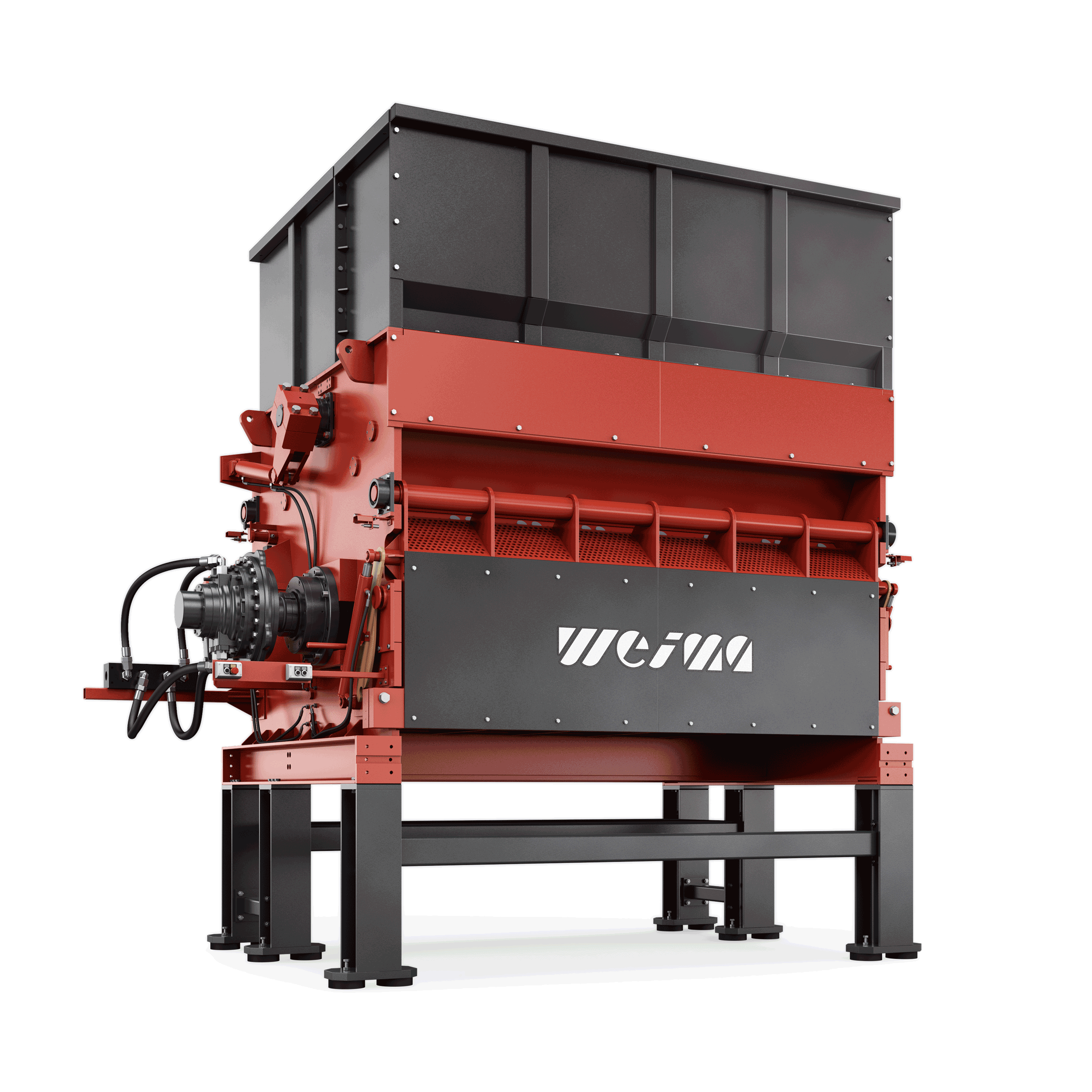
FineCut series
For secondary shredding within a multi-stage production line, we recommend our machines of the FineCut series. They take care of already pre-shredded, clean material and work with significantly higher rotor speeds. The rotor, specially designed for high speeds, is available in lengths of 1,500 mm, 2,000 mm, 2,500 mm and 3,000 mm. The shredder is equipped with an electromechanical or high-torque drive and produces grain sizes between 15 - 150 mm.
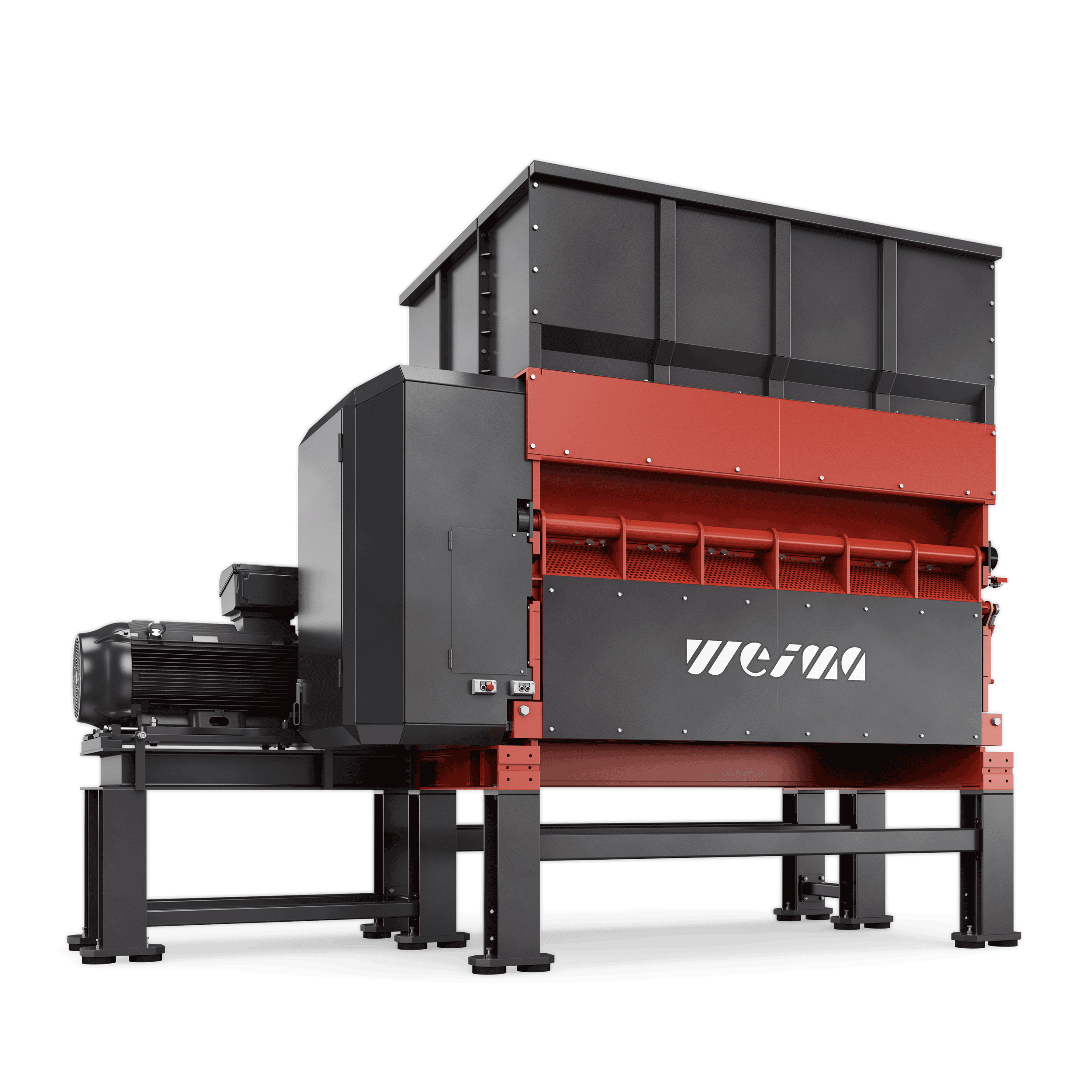
WEIMA FineCut 3000 single-shaft shredder
See for yourself
The WEIMA show room is equipped with shredding and briquetting machines of all sizes and technologies. This enables us to simulate your application as realistically as possible. You have the possibility to send us your material or visit us directly in Ilsfeld. From our gallery you have the best view directly into the cutting room. So you can observe the shredding process live.
Request appointment now
Alternatively you can send us material for testing. Click here for the form.

Textile shredding with a WEIMA PreCut 3000 @Tosung, South Korea
A powerful WEIMA PreCut 3000 single-shaft shredder shred old textiles at Tosung in Chilgok, South Korea.
Success stories
What our customers think
What are you looking for?
Explore all WEIMA solutions
Special offer
Arrange a free material trial today.
Free material trial