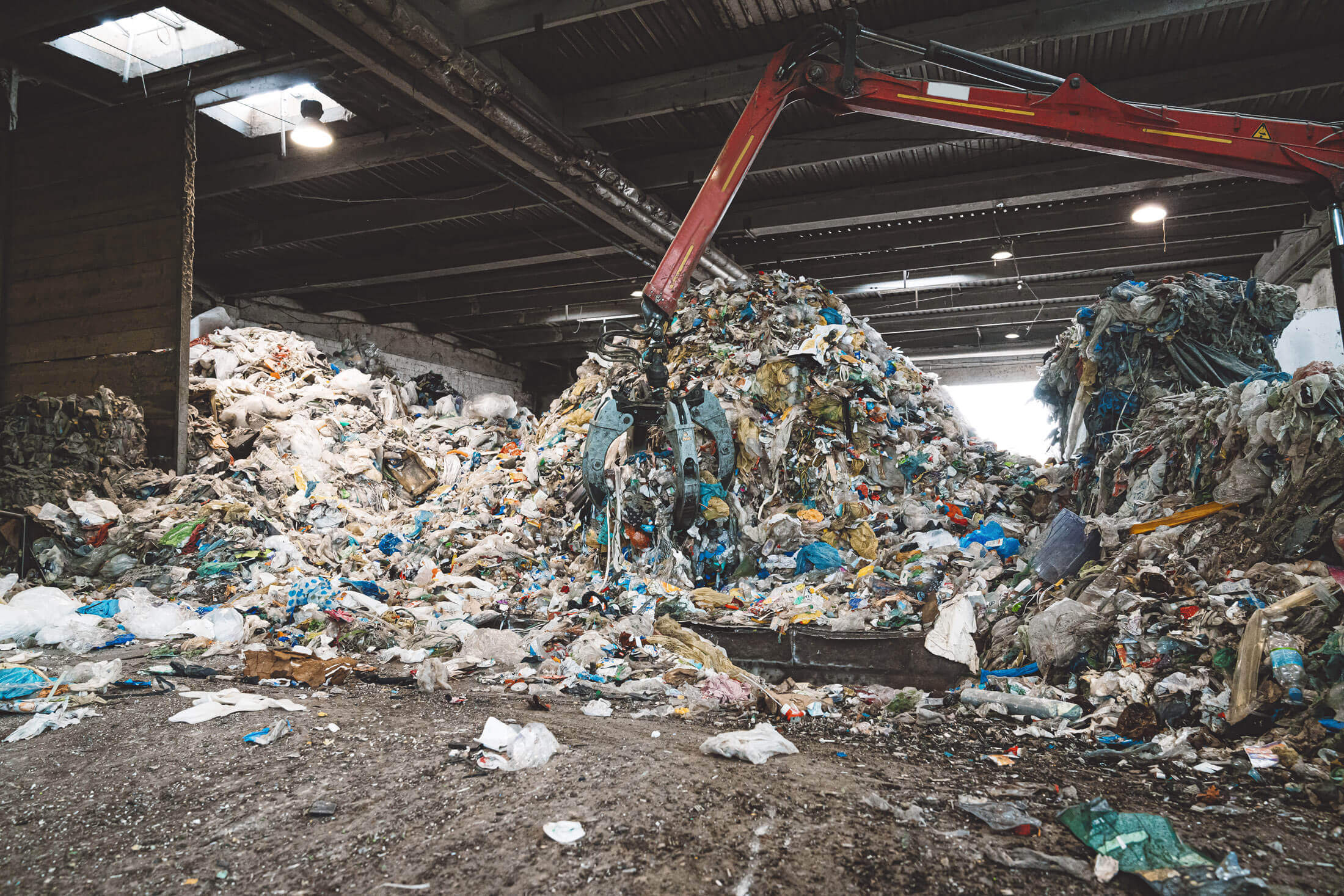
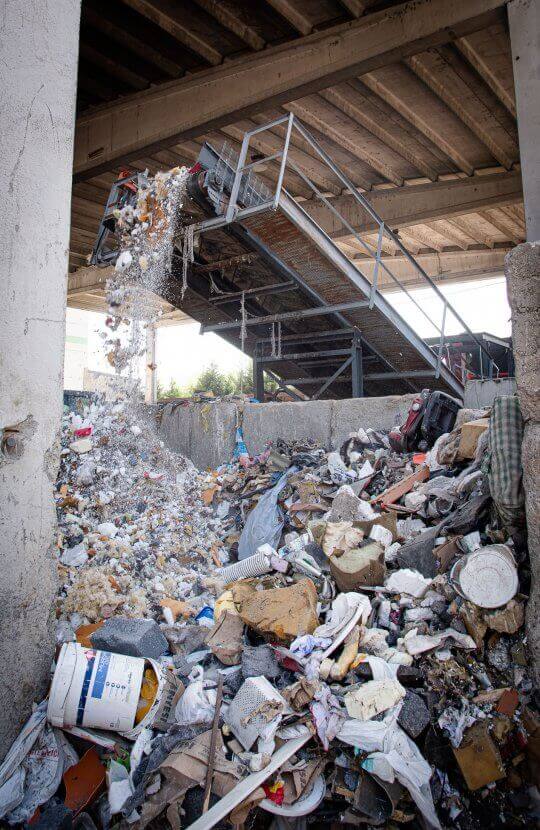
Commercial & Industrial Waste Shredders (C&I)
Information about shredders for shredding and processing of commercial and industrial waste
The recycling of industrial and commercial waste should and must be of ever higher quality, entirely in the sense of a sustainable materials cycle. Since the introduction of the German Commercial Waste Ordinance (GewAbfV) in 2003, it has been continuously optimized. Companies must adapt their waste management accordingly. Commercial waste, for example, is to be separated at the same place where it is generated. The documentation requirement has also been extended.
It is true that the Closed Substance Cycle Waste Management Act (KrWG) makes a clear distinction between private and commercial/industrial waste. However, commercial municipal waste can be very similar to private household waste. There is paper, biomass, glass, metals, textiles, packaging, residual waste and films. One major difference, however, is the treatment of hazardous waste.
Most material streams, whether they are recycled or thermally recovered, must first be shredded in one or more stages. This requires particularly robust machines, as foreign materials such as stones, sand and metals may be present. WEIMA offers the right shredders for this first process step, shredding. With up to three meters working width, many heavy duty options and drive concepts especially designed for these applications. Of course, we also offer complete plant systems from a single source. The result: safely and cleanly processed, homogeneous material streams. Made usable as refuse derived fuel (RDF) or solid recovered fuel (SRF) for the cement industry, pre-processing or co-processing.
Textile shredding with a WEIMA PreCut 3000 @Tosung, South Korea
A powerful WEIMA PreCut 3000 single-shaft shredder shred old textiles at Tosung in Chilgok, South Korea.
What is industrial waste?
When the processing of industrial goods produces residual materials that cannot be further processed, this is referred to as industrial waste. The largest quantities of industrial waste are generated by mining, the chemical industry and the construction industry. This includes construction waste, plastics and industrial sludge. Reusable material streams are recycled, which significantly reduces the amount of waste. Often, industrial waste also consists of hazardous waste, which means that it is then sent to a waste incineration plant for energy generation.
Did you know?
In 2020, approximately 47.3 million tons of commercial waste were generated in Germany.
What is commercial waste?
If you compare commercial waste with waste from private households, you will notice that they are not all that different - which is why they are sometimes referred to as commercial municipal waste. As a rule, it originates in commerce, trade, industry or public institutions such as hospitals or government offices. What exactly is considered commercial waste and how it is to be collected, labeled, documented and disposed of has been regulated in Germany since 2003 by the Commercial Waste Ordinance (GewAbfV). For example, most companies still have to separate their waste on site into: Paper, wood, glass, metals, textiles, plastics, films and biomass. This is the only way to ensure that valuable residual materials can also be efficiently processed or recycled. Despite all this, Germany still produces around 6 million tons of so-called mixed waste every year, where no sorting has taken place beforehand. As a result, 90 percent of this mixed commercial waste ends up in incineration as refuse-derived fuel (RDF) and is thus lost to the cycle.
Source: STMUV Bayern
Source: Deutsche Umwelthilfe
Source: Thüringen Recycling
Practical examples and references: Commercial Waste | Industrial Waste Shredders
WEIMA delivers over 1,000 machines per year. Many of them are used for the material and energetic treatment of commercial and industrial waste. You can find an excerpt of current reference projects here:
What counts as mixed commercial waste?
- Plastic
- Rubber
- Corrugated cardboard, paper
- Waste wood (Class 1-3)
- Cork
- Metal
- Styrofoam
- Packaging
- Textiles
- Composites
What does NOT count as commercial waste?
- Construction waste
- Biomass
- Kitchen waste
- Hazardous waste
- Roofing felt, mineral wool, asbestos
- Waste wood (starting from Class 4)
- Used tires
- Liquids such as paints, varnishes, oils
Request the right shredder for industrial and commercial waste
Request quote
How is commercial waste | industrial waste processed, recycled and disposed of?
After in-house collection in containers or waste garbage cans, commercial waste is transported to special facilities for processing. On site, pre-shredding first takes place. This can be implemented with a twin-shaft shredder (for example a WEIMA M8.28 Pre-Shredder) or a single-shaft shredder (for example a shredder from the WEIMA PreCut series). As a result, the volume is significantly reduced. Subsequently, the pre-shredded material can be screened and sorted. As politicians continuously aim for higher quotas for material recycling, automatic sorting technologies are becoming better and more precise. To separate FE fractions, overband magnets or permanent magnets are used. For non-ferrous metals, so-called eddy current separators (eddy currents) are used. All other materials can be detected using the latest sensor technology. These can be induction sorting systems or near-infrared systems (HSI for Hyper Spectral Imaging).
Post-industrial film shredding with a WEIMA W5.22 @ EcoFib, Canada
A WEIMA W5.22 shreds post-industrial film at EcoFib in Canada.
Once all material streams have been cleanly separated, sorted and shredded, they can be passed on to recycling companies. Used packaging films can be turned into new ones again, just as used paper can. Waste wood, for example, can be used for chipboard production. Those materials that cannot be recycled (due to pollution or other contamination) are ultimately fed into energy and heat generation – although this rate is expected to drop significantly. The primary goal remains the circular economy.
Challenges in the shredding of commercial and industrial waste
Our industrial and commercial waste sometimes contains materials and things that do not belong there - and make processing correspondingly difficult. These include stones, soil, large pieces of metal, sand, ash, or pollutants of various categories. So the better the pre-sorting, the less wear can be expected during the shredding process. Nevertheless, maximum robustness, powerful drives and easy maintenance are and remain the trump cards for industrial shredders in order to avoid unpleasant downtimes. Here, WEIMA can rely on a broad and decades-long wealth of experience.

Shredding for RDF production
Stand-alone operation or integration into a production line
Unlock your waste-to-energy potential! Depending on your requirements, we supply you with the right shredder for your shredding task. If required, WEIMA also offers a multi-stage system solution in the form of a plant. We are assisted in this by an extensive supplier and service network that we have built up over the past decades.
This includes specialists from the fields of conveying, sorting, separation, screening, washing, metal detection, extrusion, heating and granulation. As a joint project team, we have already mastered hundreds of major tasks all over the world.
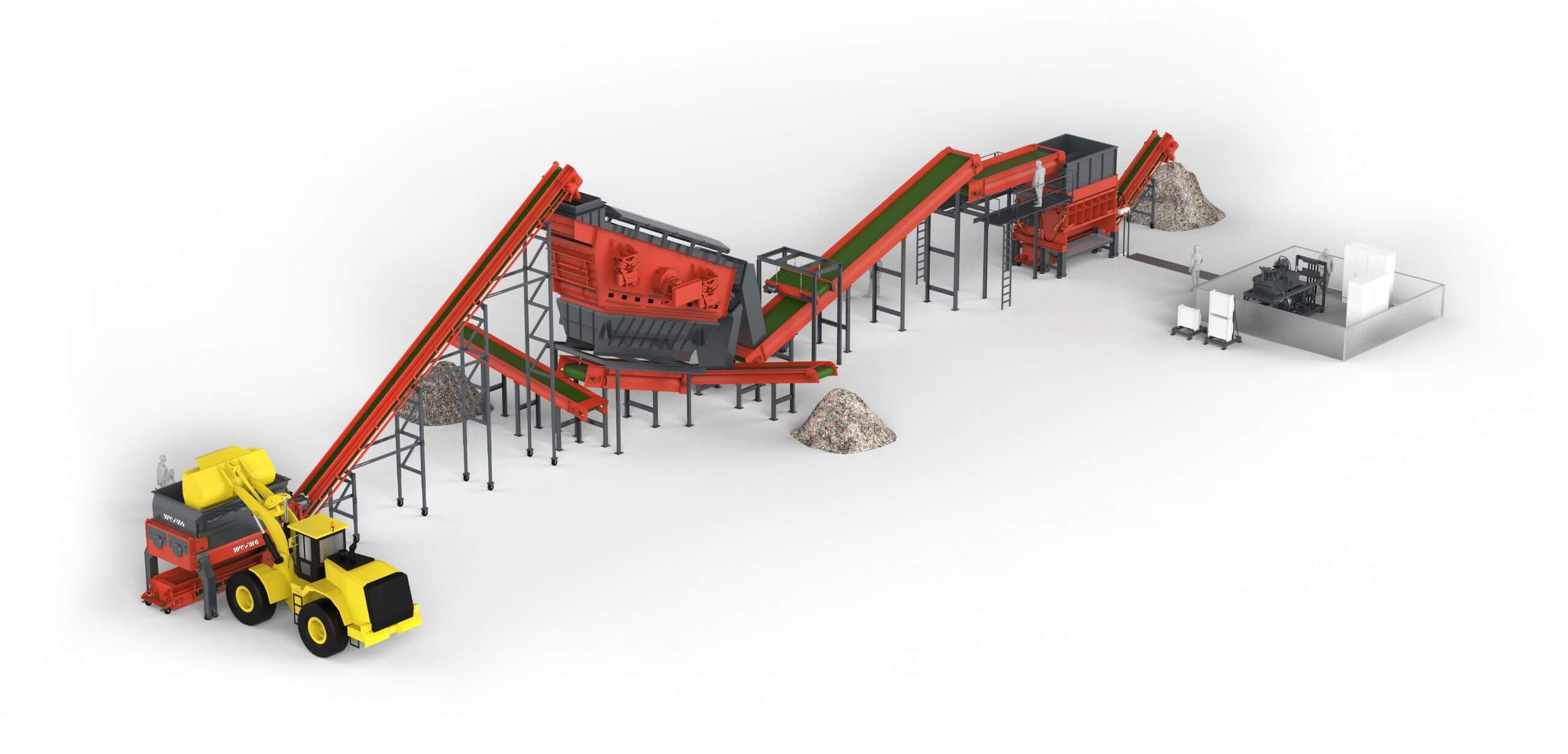

Alternative fuels for cement production
The cement industry has a very high demand for energy. This can increasingly be met with refuse-derived fuels. The focus is on the combustion of alternative fuels in caliciners, preburners and kilns. In order to reduce energy costs, cement manufacturers are increasingly focusing on increasing the proportion of alternative fuels used in energy production. Compared to conventional materials, the thermal utilization of alternative fuels has better physical combustion properties and better burnout in the kiln. In general, the better the alternative fuel used, the more efficient the production of high-quality clinker.

Alternative Fuel AF RDF
What is Pre-Processing?
- As a rule, waste cannot be used directly for recycling in cement kilns, but must be prepared beforehand. The treatment process, also called pre-processing, includes the shredding, mixing and drying of waste. The use of WEIMA shredders in pre-processing enables consistently homogeneous particle sizes of the most demanding material. This guarantees a stable fuel that meets the technical requirements of cement production.
What is Co-Processing?
- The term co-processing describes a globally recognized technology used in energy-intensive industries (EII) such as cement production to recycle waste and industrial by-products for energy and materials. The mineral materials in the waste replace primary raw materials (e.g. limestone) in the cement kiln, while the combustible materials provide the energy needed to produce clinker. No residues are produced in the process, and highly toxic waste is also destroyed. Co-processing thus makes it possible to avoid landfilling and waste incineration of wastes such as sewage sludge, solvents, plastics from industry or mineral wastes.
What are the advantages of Co-Processing?
- Co-processing in the context of cement production has many advantages: The high temperatures and long residence time in the kiln completely destroy even toxic residues. No residual materials are produced that have to be recycled or even landfilled. The use of co-processing technology also avoids the use of fossil fuels and consequently reduces greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, cement manufacturers can massively reduce their energy costs thanks to secondary fuels from waste.
What is Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF)?
For the production of Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF), additional process steps are usually necessary, as higher quality requirements for its production have been defined at European level. The essential properties of a classification include the calorific value as well as the chlorine and mercury content. This results in five quality classes in order to be able to designate processed waste as Solid Recovered Fuel.
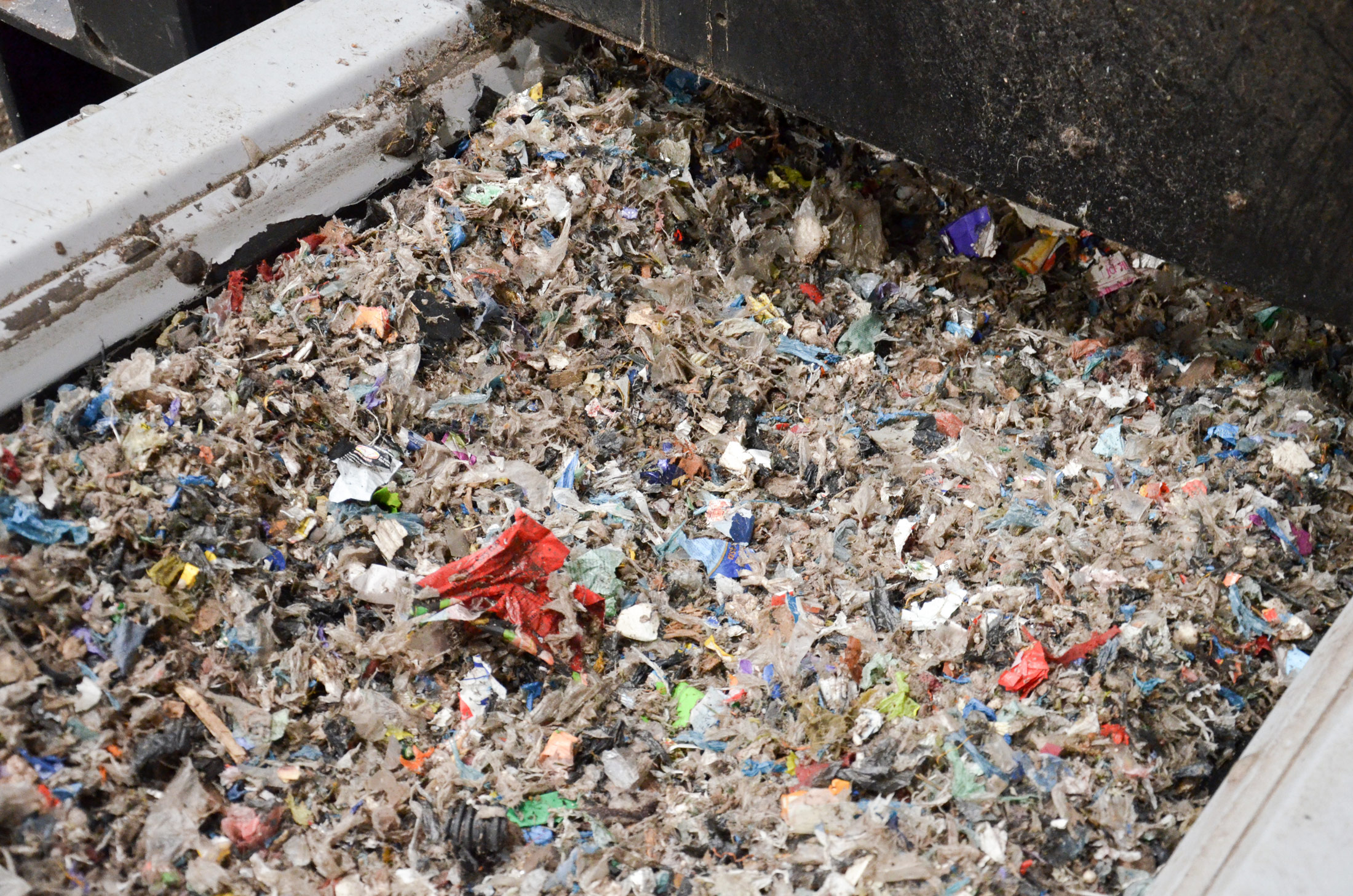

Secondary fuel for the calciner firing
What is refuse derived fuel (RDF)?
WEIMA waste shredders are ideal for the production of medium and high calorific RDF (refuse derived fuel) or calciner fuel. These are fuels obtained from household, industrial and municipal waste. The different quality requirements depend on the thermal process. Typical processing steps for the high-calorific fraction include pre-sorting, pre-shredding, air classification and metal separation. Sensory sorting and drying are also possible. In most cases, refuse-derived fuel is used together with conventional fuels, e.g. in cement, lime, coal and industrial power plants.
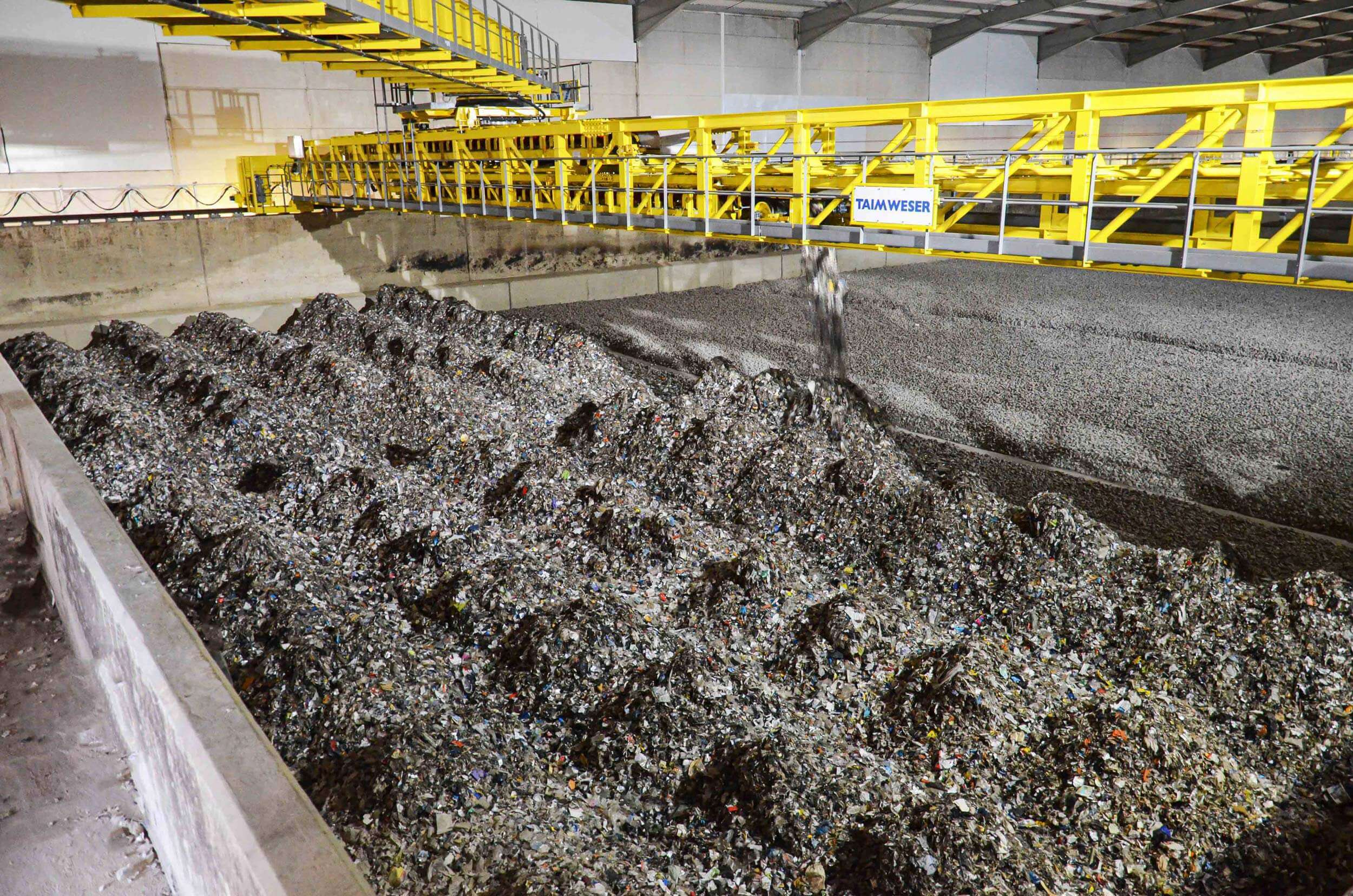

RDF silo storage
How does the Mechanical-Biological Waste Treatment (MBT) work?
This generally involves household waste, MSW or commercial waste similar to household waste. This is initially collected by disposal companies and transported to a central location for waste treatment, disposal or recycling. Typically, household waste contains a high proportion of organic matter. After rough screening, this is shredded and then divided into different fractions by screening. The coarse fraction (films, paper, hard plastics, wood, etc.) is usually used as fuel in RDF power plants because of its high calorific value. The fine fraction (organic substances), on the other hand, is usually further biologically treated. Gases produced in this way can be used for energy.

WEIMA PowerLine shredder
PowerLine: universal shredder with single-shaft technology for pre- or post-shredding
Performance that pays off. The PowerLine series takes on any form of waste, even contaminated materials. Ideal as a shredder in multi-stage plants: After sorting out materials not suitable for RDF, the pre-shredded material can be optimally processed in the secondary shredding stage. Can be equipped with hydraulic drive, direct drive or power belt drive.
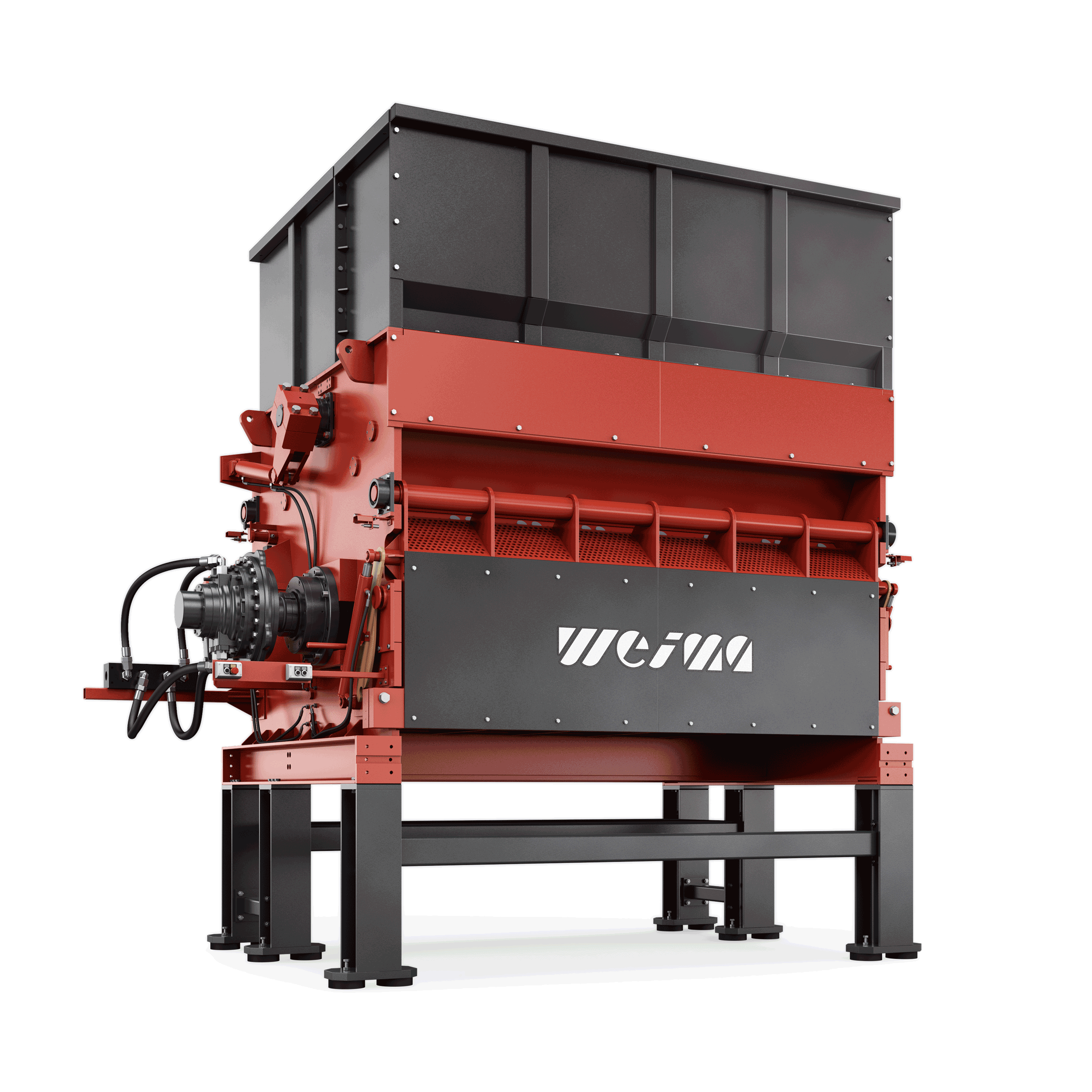
WEIMA PowerLine shredder
M8.28: Rugged heavy-duty primary shredder with twin-shaft technology
The WEIMA M8.28 shredder with twin-shaft technology is ideal for use as a pre-shredder. It is characterized by high throughput rates with maximum robustness and shreds a wide variety of coarse material streams for further recycling. Typical next process steps are sorting and separation, followed by secondary shredding.

M8.28 primary shredder with hydraulic drive
FineCut: High-throughput secondary shredder for RDF production
Smallest particle sizes, best sales opportunities. The FineCut is the ideal secondary shredder for multi-stage plants. Thanks to high speed, extreme throughputs are realized. The fine particle sizes of the shredded material perfectly meet the increasing demand for ever higher RDF qualities.
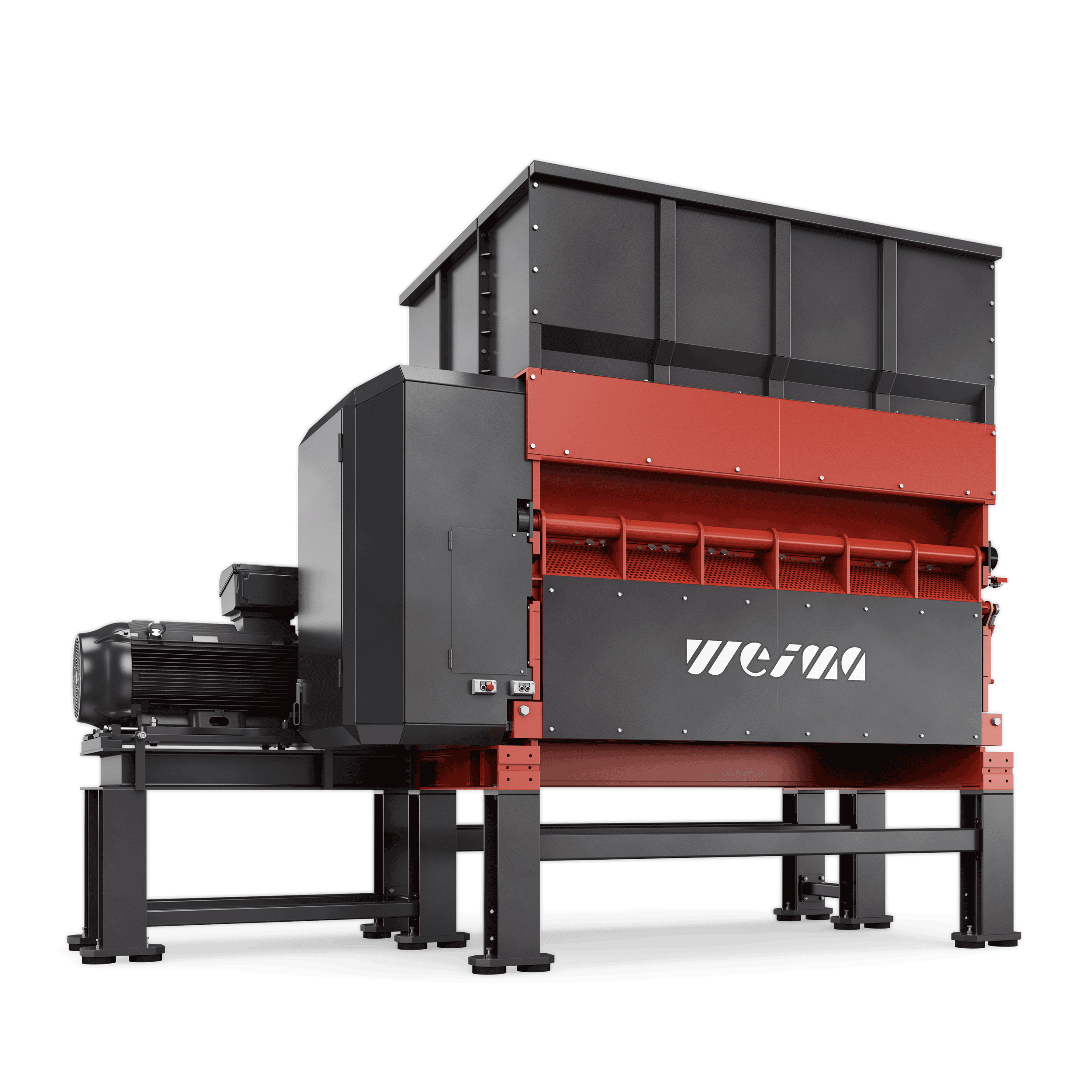
WEIMA FineCut 3000 single-shaft shredder
Only at WEIMA.
Heavy duty machine designs
for long service life
Easy maintenance
for minimal down times
Various drive options
for maximum throughput
Fast service and support
for highest customer satisfaction
Everything from one source
machines, conveying technology, metal detection, support, spare and wear parts for customized solutions

WEIMA headquarters Ilsfeld (Germany)
Convince yourself.
The WEIMA showroom is equipped with shredding and compacting machines of all sizes and technologies. This allows us to simulate your application as realistically as possible. You have the possibility to send us your material or to visit us directly in Ilsfeld. From our gallery you have the best view directly into the cutting room. This allows you to observe the shredding process live.
Request appointment now
Alternatively, you can send us material for testing. Click here for the form.
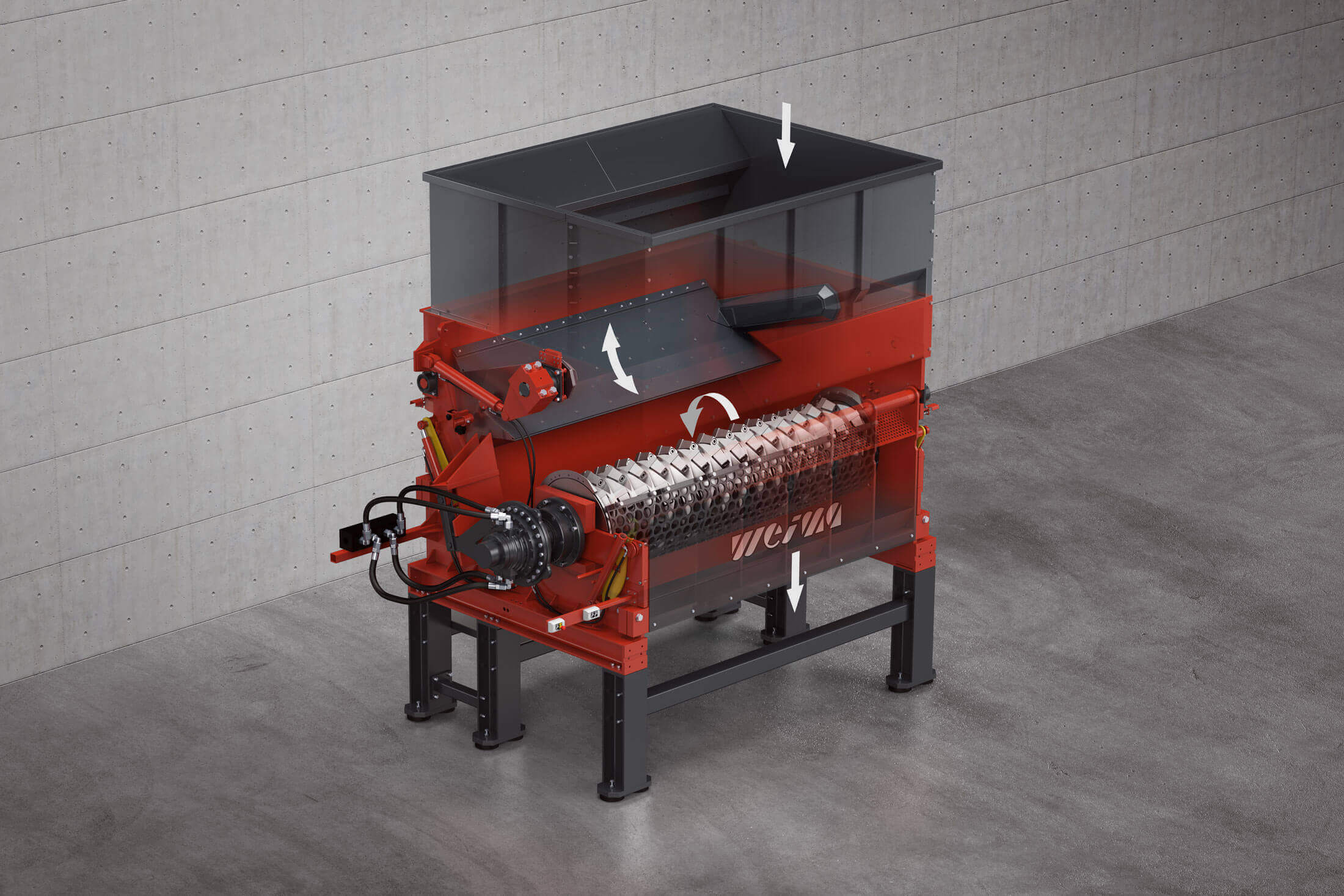

WEIMA PowerLine 3000 waste shredder



