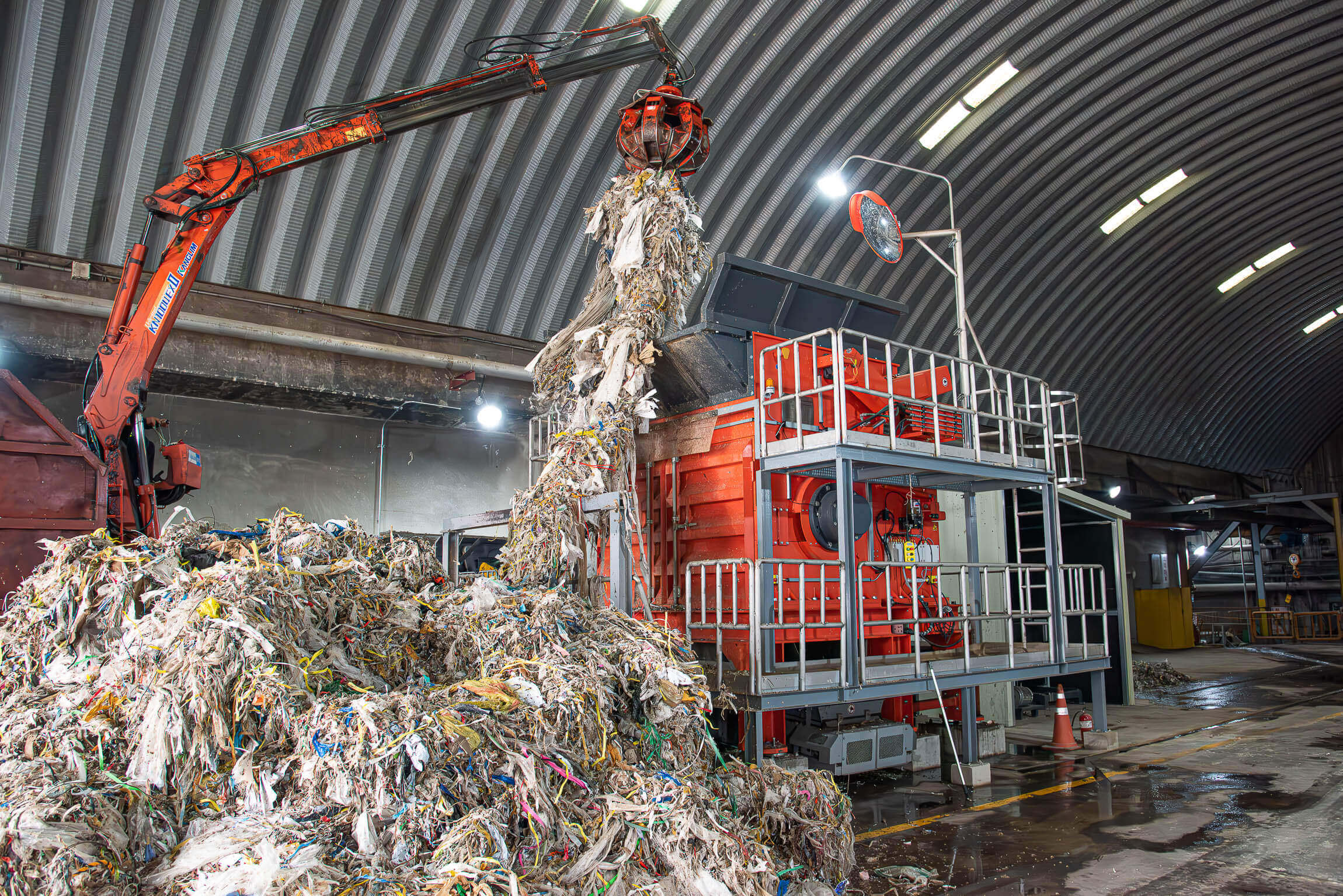
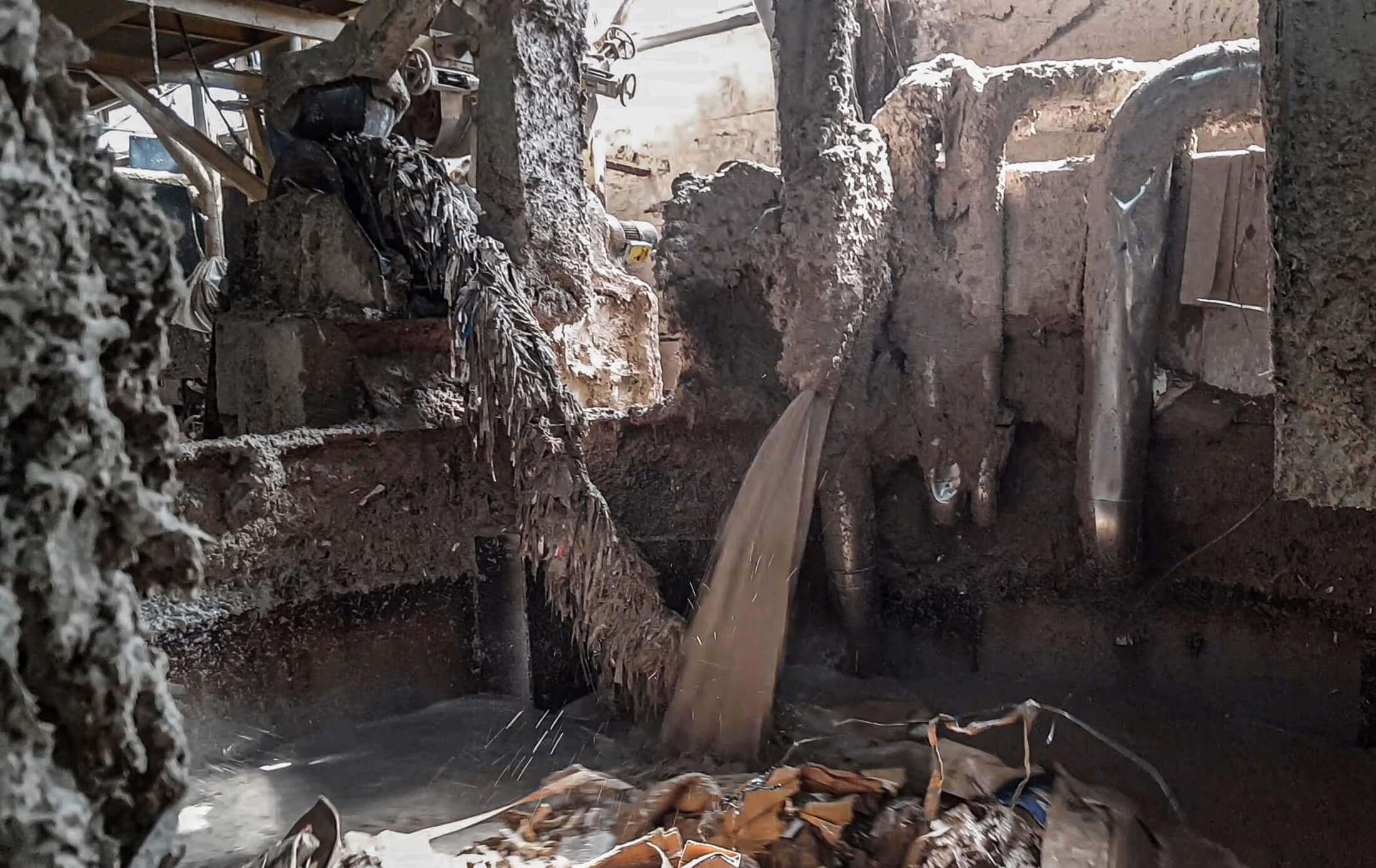
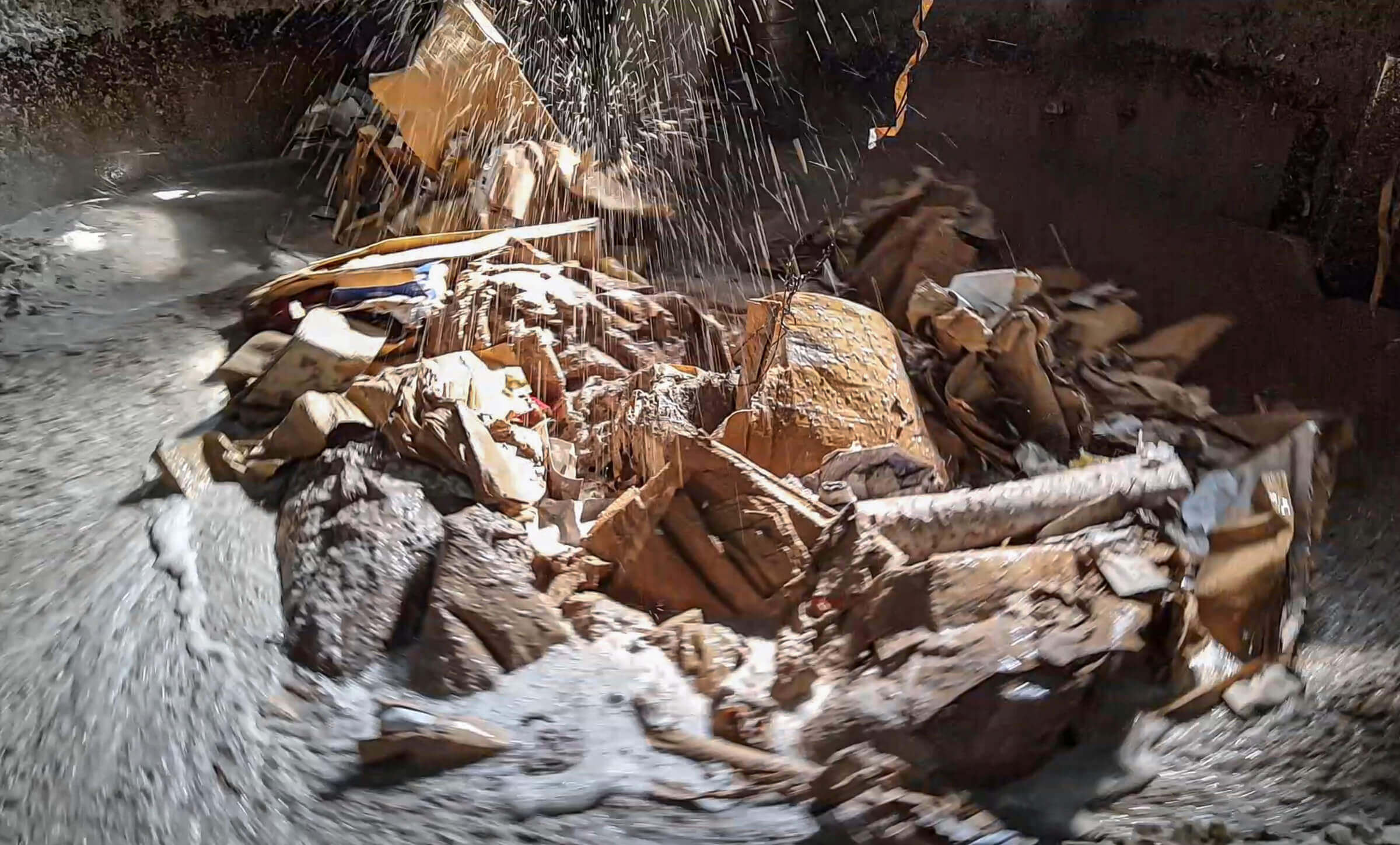
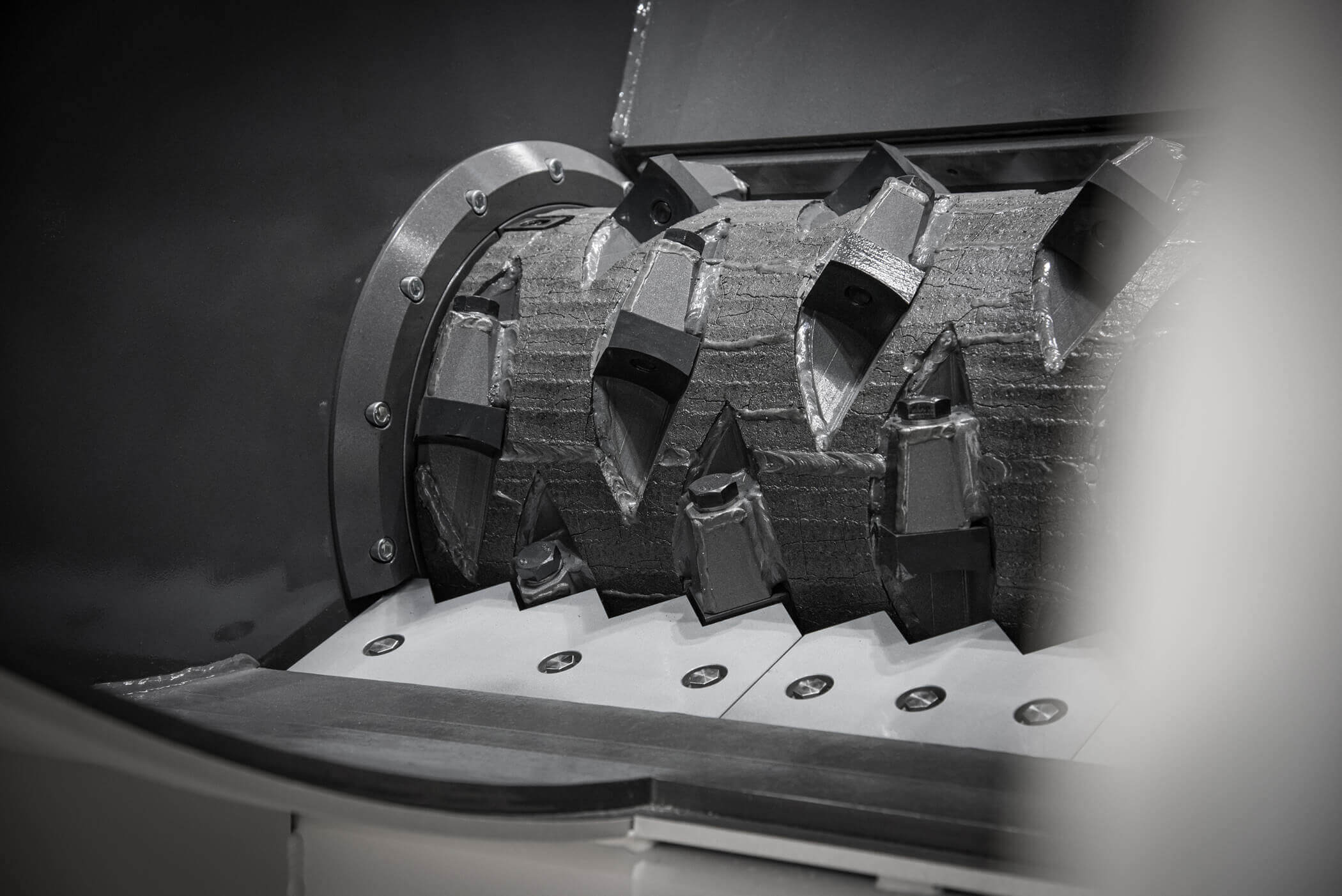
Shredding pulper ropes
Information on proper reject processing
The proportion of waste paper in the production of paper is continuously increasing. In Germany, the paper industry produces around five million tons of recyclable waste each year. These residues often originate from the waste paper and cardboard that is collected, pressed into bales and delivered baled. Disposal without prior material processing has always caused considerable costs for paper manufacturers.
This waste is usually referred to as pulper waste – meter-long pulper rope cuttings made of metal and plastic, or loose rejects. For its recycling, special know-how and robust shredding technology is required to separate the different material flows from each other. After all, pulper rejects contain valuable materials. The plastic can be used as substitute fuel (RDF) for energy generation. The metal wires can be reused as recycling material. But also non-ferrous metals such as copper, aluminium etc. can be recovered in the process by means of an eddy current separator.
WEIMA PreCut 2500 shreds meter-long pulper ropes and rejects from paper recycling
What are pulper ropes?
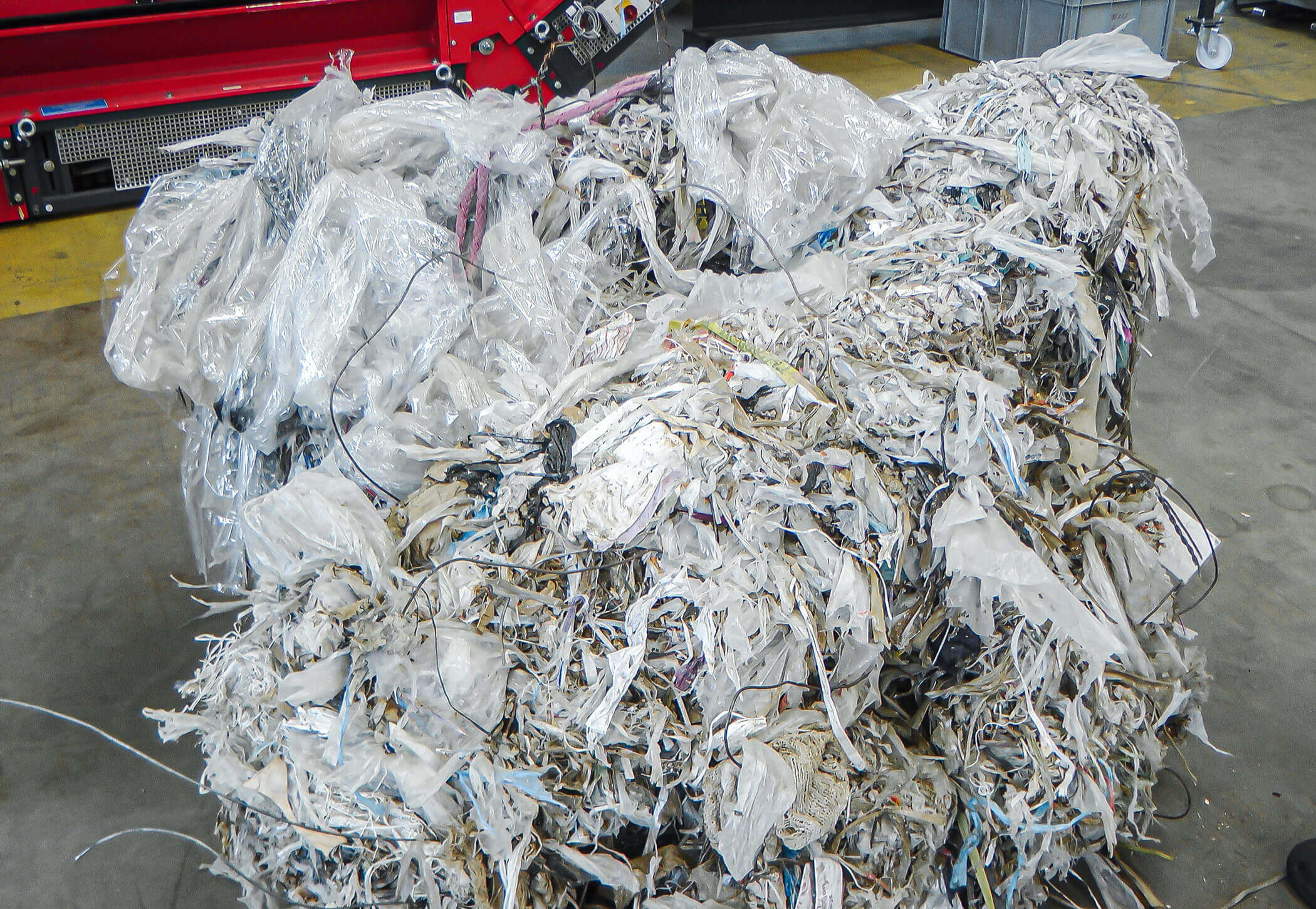
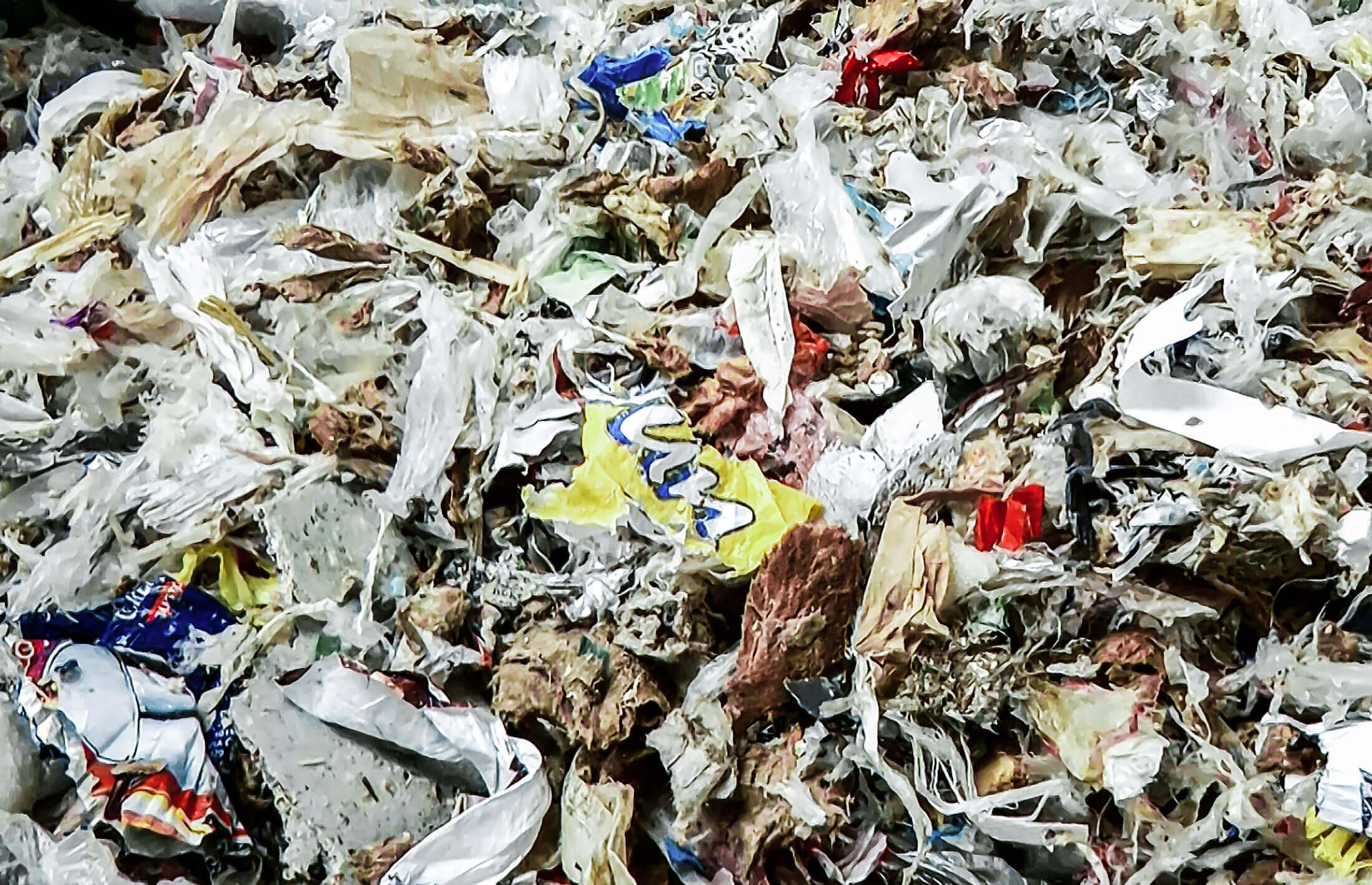
Pulper braids, also known as rejects, are a waste product of paper production. They can consist of up to 50 % metal wires. The reason for this is the delivery of waste paper in the form of pressed bales. To keep them in shape, wires are used, but also plastic straps. Pulper ropes can often be several meters long and also contain materials such as plastic film, string, wooden parts and small plastic parts.

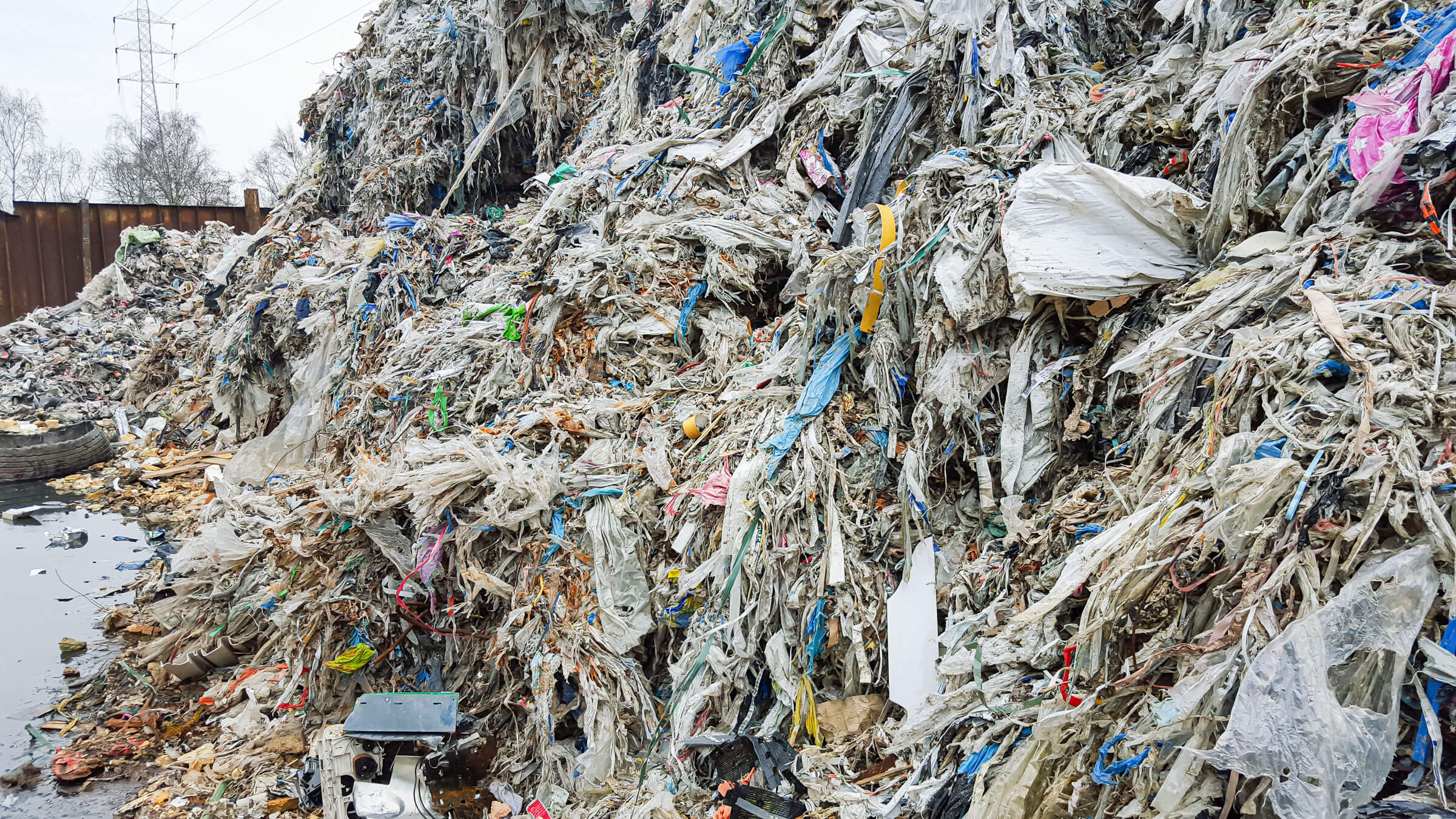
Six meter long pulper reject rope
How are pulper ropes and rejects formed?
In paper production, waste paper, cardboard and new raw materials are dissolved and defibered with process water in so-called pulpers (also pulping drums). During this process, unwanted foreign matter such as wires, stickers, cords, films, small wooden and plastic parts or other non-soluble papers are added to the pulper.
A catching device is used to prevent these impurities from getting caught together during paper production and then having to be removed in a time-consuming and costly process using a crane. For this reason, a long rope is usually lowered into the stirring vat, with which the wires and plastic parts get caught in the pulper rope (reject). This can then be removed by means of a ragger. At regular intervals, the pulper rope is slowly and continuously pulled out of the vat. Gradually, a pulper rope several meters long is created.
In case only relatively small ropes are formed, the use of a collecting arm is also recommended. It rotates in the opposite direction to the pulper and picks up the rejects with the help of rakes and hooks on the catch arm.
How can pulper ropes be disposed of economically?
The disposal of pulper ropes without prior shredding and sorting is very costly and not very sustainable – after all, they contain considerable material and energy potential that can be used economically. The resulting plastic fraction in particular provides the ideal conditions for use as a substitute fuel (RDF). For example, brick or cement manufacturers and power plant operators use this high-calorific secondary fuel for their plants, kilns and calciners. But also paper manufacturers have already discovered their own use of this fuel and are thus becoming less dependent on fossil fuels.

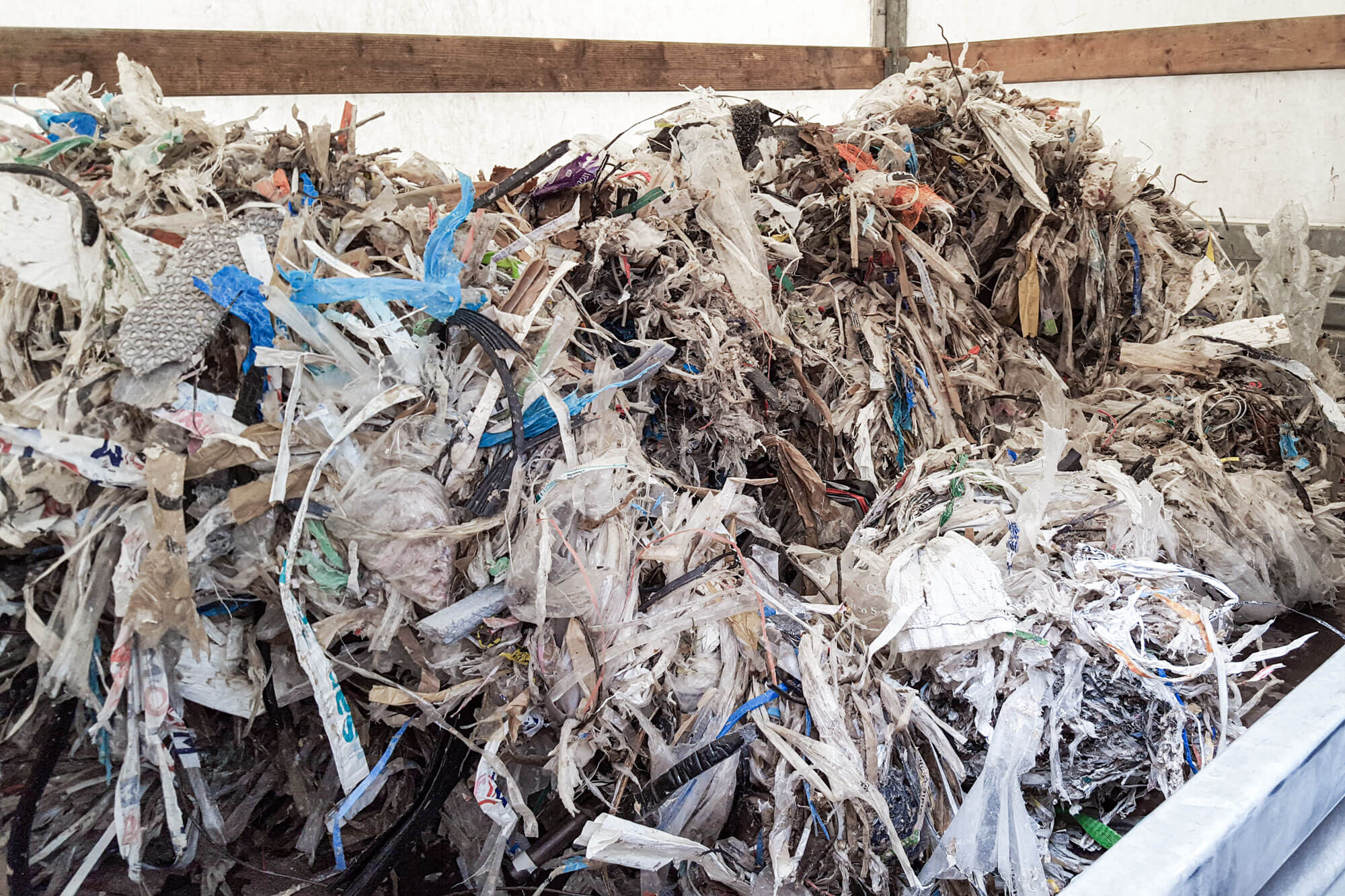
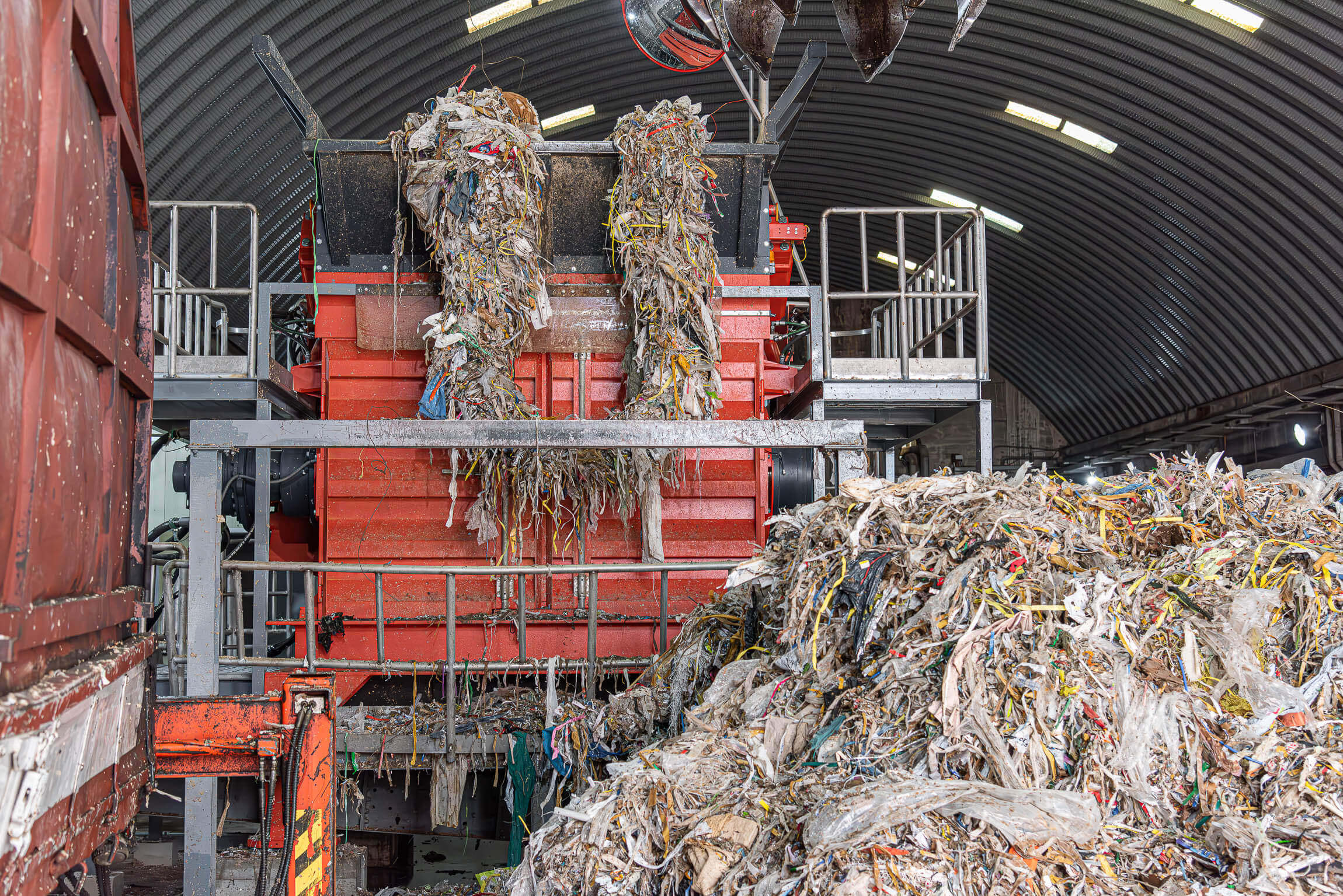
Pulper rupe in WEIMA shredder
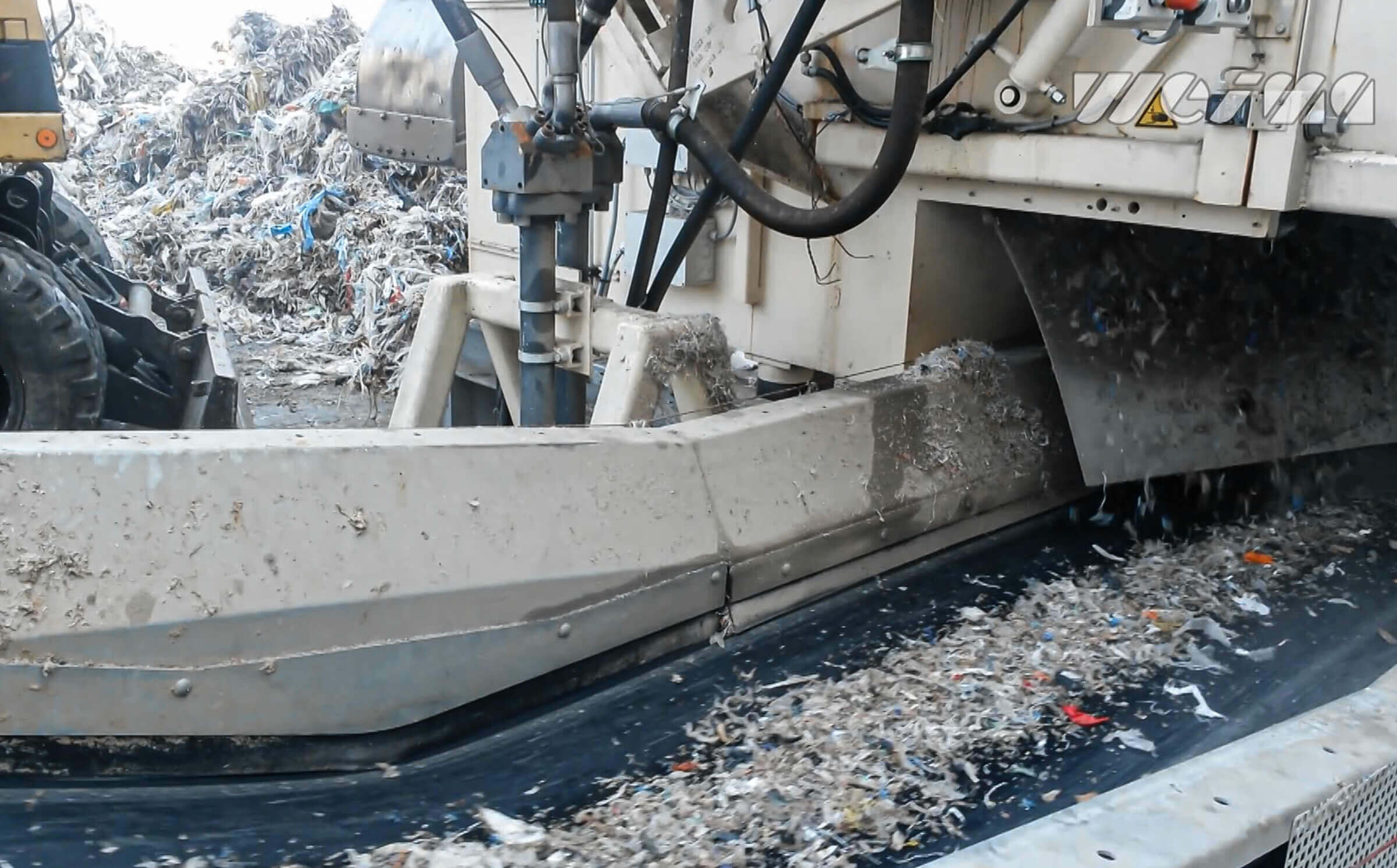
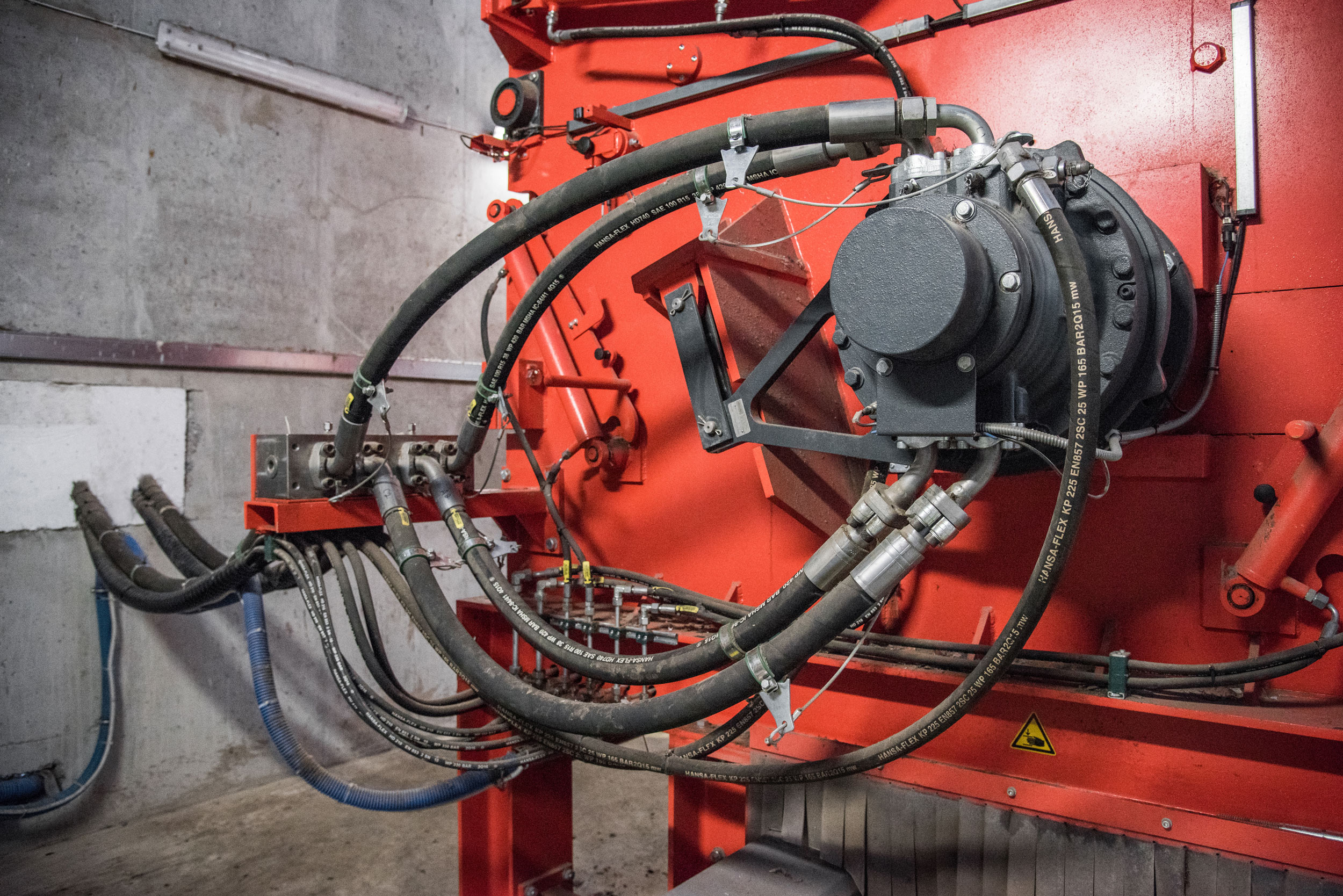
Pulper rope shredding with a WEIMA PreCut 2500
A WEIMA PreCut 2500 shredder shreds big pulper ropes from paper recycling.
Of bears, rejects and pulper
Bears
Paper production can be very creative. For example, the term bear is used to describe the unwanted tangles of wire and plastic parts that form in the pulper. These can only be removed with great effort by crane. The more convenient solution is the formation of pulper ropes, which can be removed via a support roller.

Secondary fuel (RDF) from pulper rejects
Successful pulper waste shredding in Turkey at KMK Paper
KMK Paper, one of the largest manufacturers of cardboard in Turkey, recycles more than 100 tons of pulper waste and loose scrap from production each day at their plant. A particularly clever feature is that the resulting substitute fuel is reused as an energy source for the company's operations.

Murat Göktepe, official WEIMA dealer in Turkey, in front of two WLK 25 SJ shredders
Pulper
Pulper refers to the up to 100 m³ big dissolving drum, which is similar to a kitchen machine's stirring vat. With the help of special process water, waste paper, cardboard and paperboard is dissolved in it. The defibered mixture forms the basis for the production of new paper. By the way: The predecessors of today's pulper vessels were formerly known as hollander.
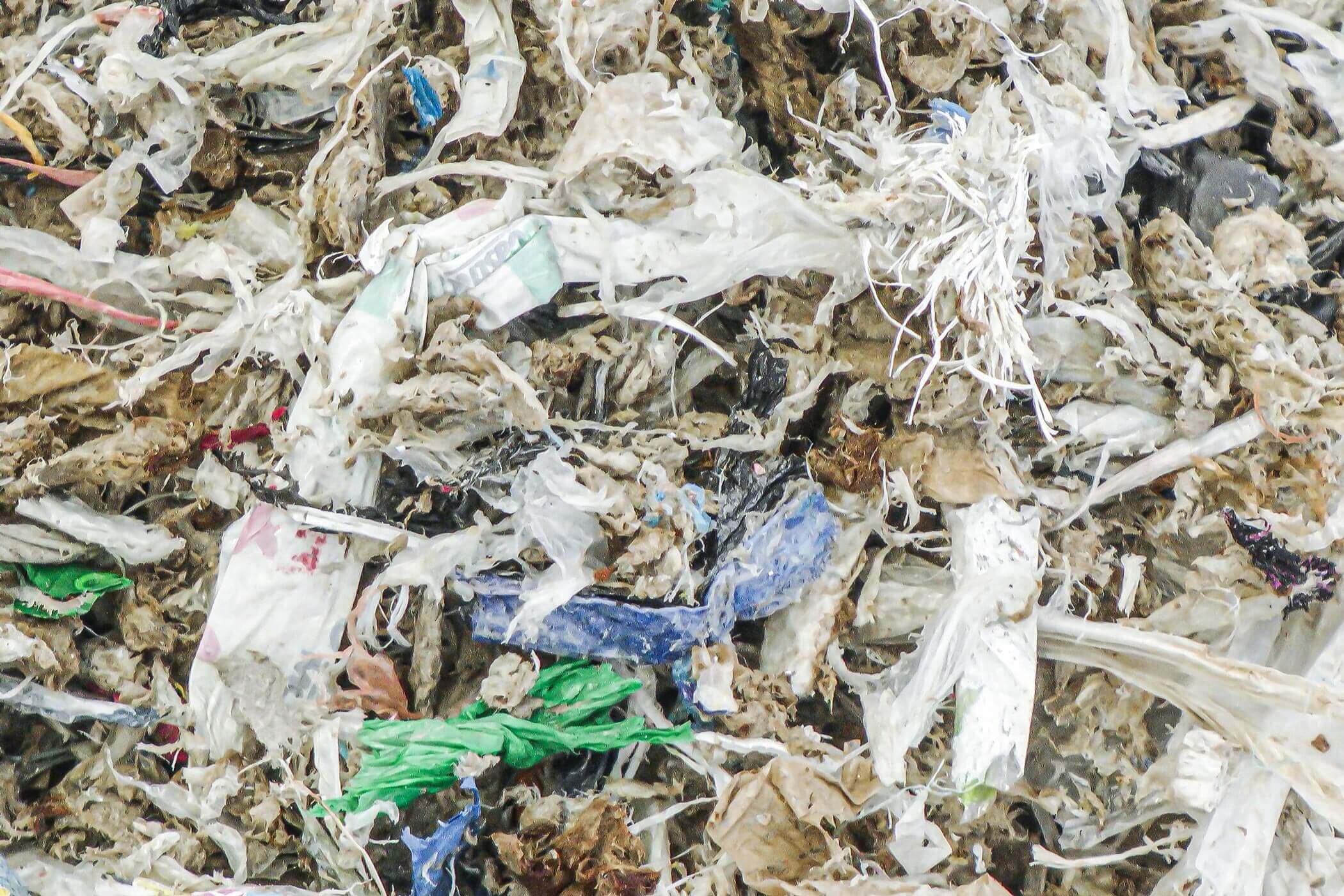
Rejected foreign fractions
Rejected foreign fractions are materials that are not usable for paper production and that accumulate during waste paper processing. They include the most diverse material fractions. For example, plastics such as films, packaging, composites as well as paper clips or textile material from book covers. They are mainly used as substitute fuel for heat generation.
Inquire about a pulper shredder today
Request a quote
How does shredding work?
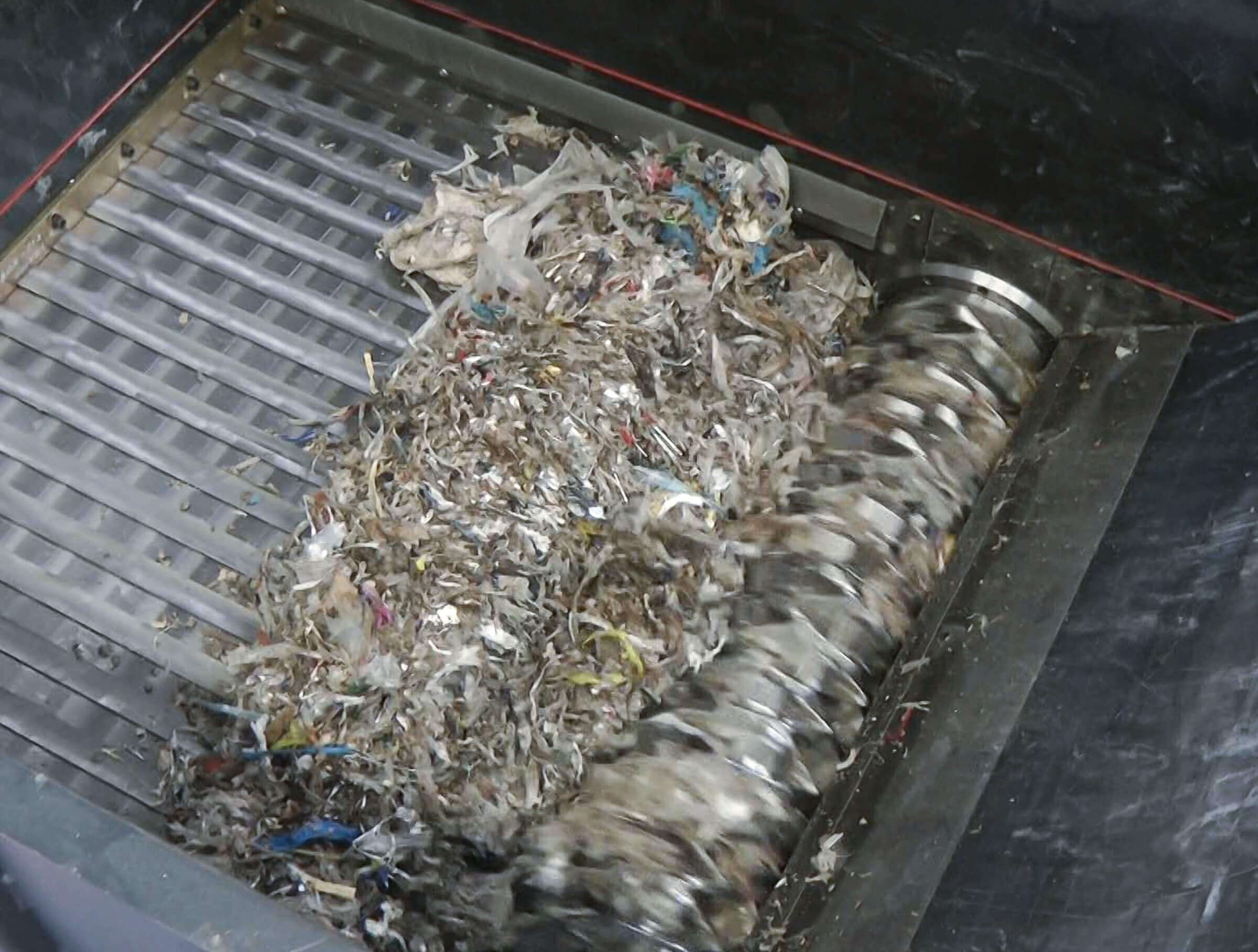
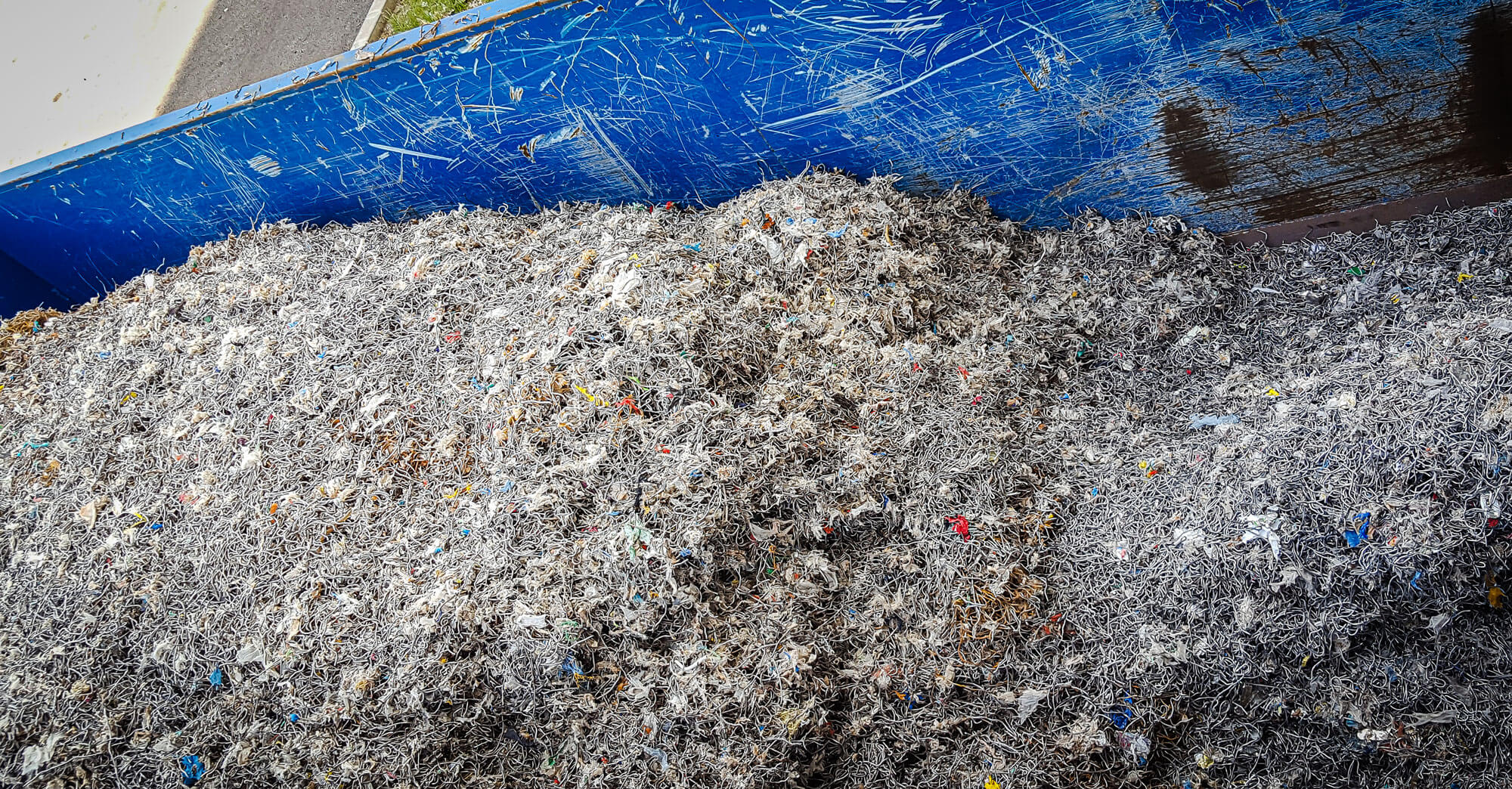
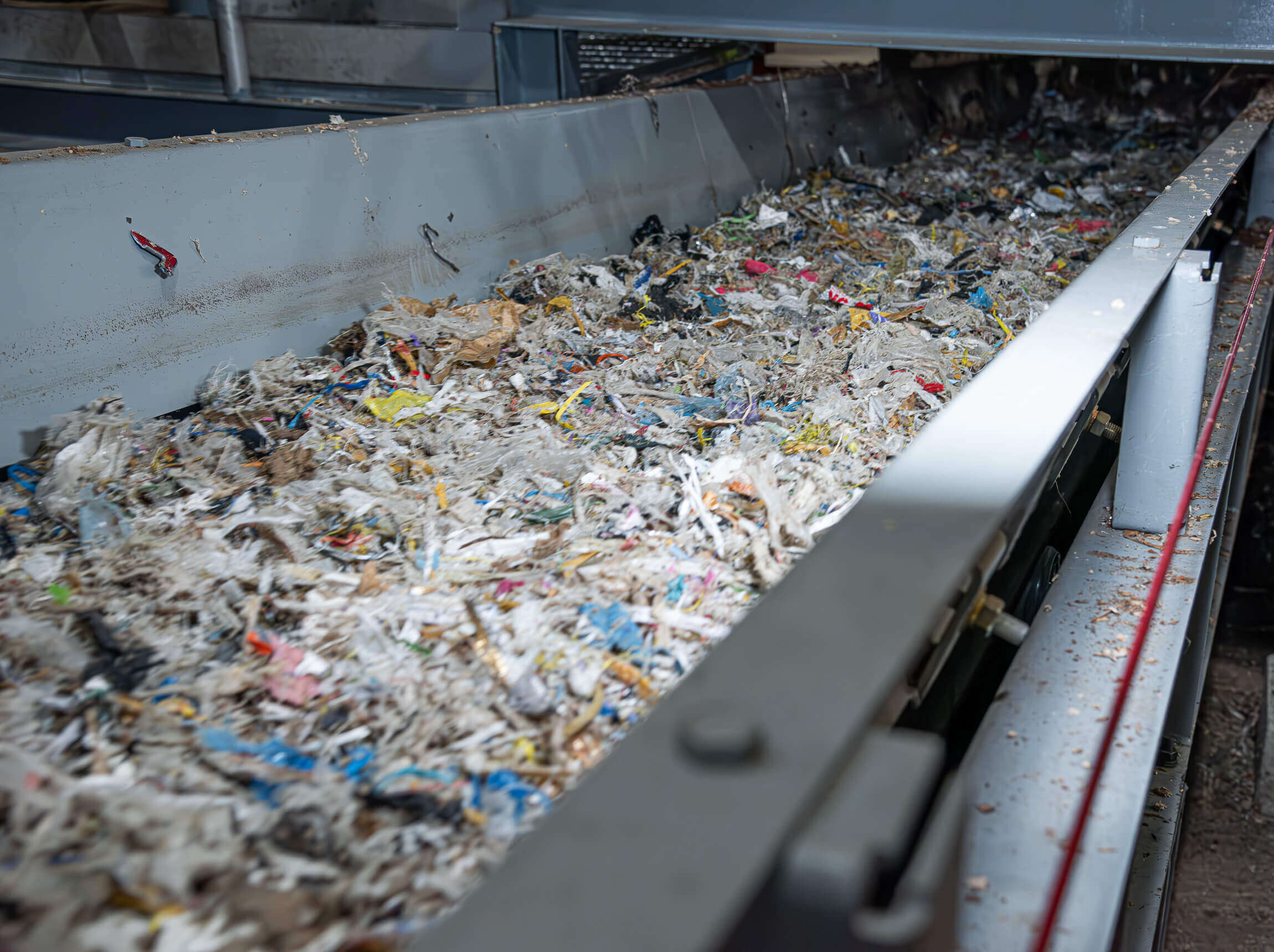
Pulper rope sections can be fed directly by wheel loader, crane or conveyor belt into the hopper of the WEIMA single-shaft shredder without pre-treatment or manual preparation. This saves time and personnel. After the paper rejects have been shredded to a homogenous grain size and separated from metal residues by means of an overband magnet, the material can be stored or dried. It can then be used thermally as a high-quality substitute fuel, refuse derived fuel (RDF) or solid recovered fuel (SRF).

Pulper rope cuttings in the WEIMA shredder
Did you know?
In Germany, an average of 760 kg of recovered paper was used to produce one ton of paper in 2018. Tendency: rising.
Example applications from the secondary fuel industry and paper production
W5 series: Maintenance-friendly all-rounders with swing ram
With working widths of 1,400 mm, 1,800 mm or 2,200 mm, the W5 series takes on a wide variety of materials. The inspection flap and the lift-up screen basket make the single-shaft shredder particularly easy to maintain. Thanks to the wide conveyor belt cutout, large quantities of shredded material can be transported away quickly and cleanly.

WEIMA W5 shredder interior view
Swing ram for particularly good material feed
The material feed using swing technology makes the shredder particularly compact, simplifies maintenance and allows more aggressive material feeding. Material already slides towards the rotor by gravity and is then pressed against it continuously or intermittently by the hydraulically movable swing ram. For even more aggressive feeding, the swing can optionally be equipped with a pusher.

Cilindro de trituração WKS
WEIMA W5.22 single-shaft shredder shreds pulper ropes and rejects
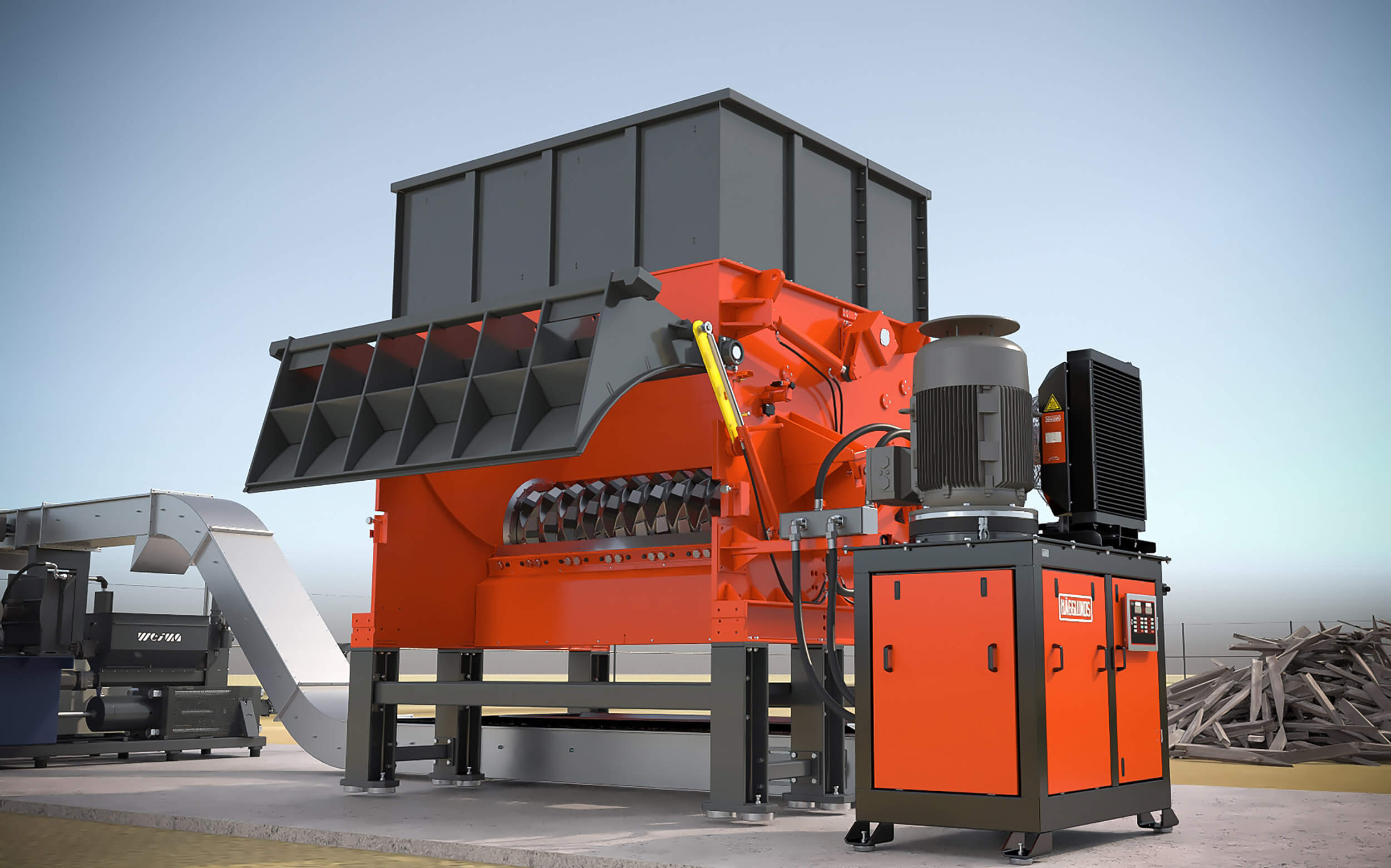
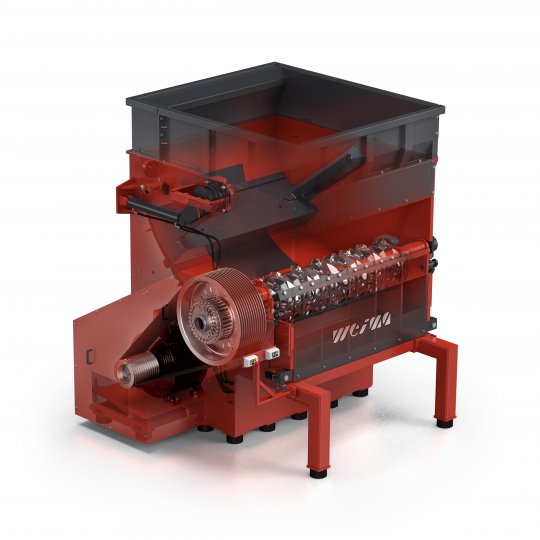
PreCut series: For extreme throughput requirements
The PreCut 2000-3000 series is characterized by extremely high throughput rates. PreCut machines are often used as pre-shredders in multi-stage processing plants, but are also suitable as stand-alone solutions. Thanks to Vautid wear protection, the solid PreCut rotor is particularly resistant to foreign matter. Reinforced side walls make the frame of the shredder extremely solid.

WEIMA PreCut single-shaft shredder
PowerLine series: Sharp cuts
The machines of the PowerLine series are universally applicable. Variable equipment and sizes allow an exact adaptation to your special requirements. The counter knives are user-friendly adjustable from the outside and protected by an additional cover plate.
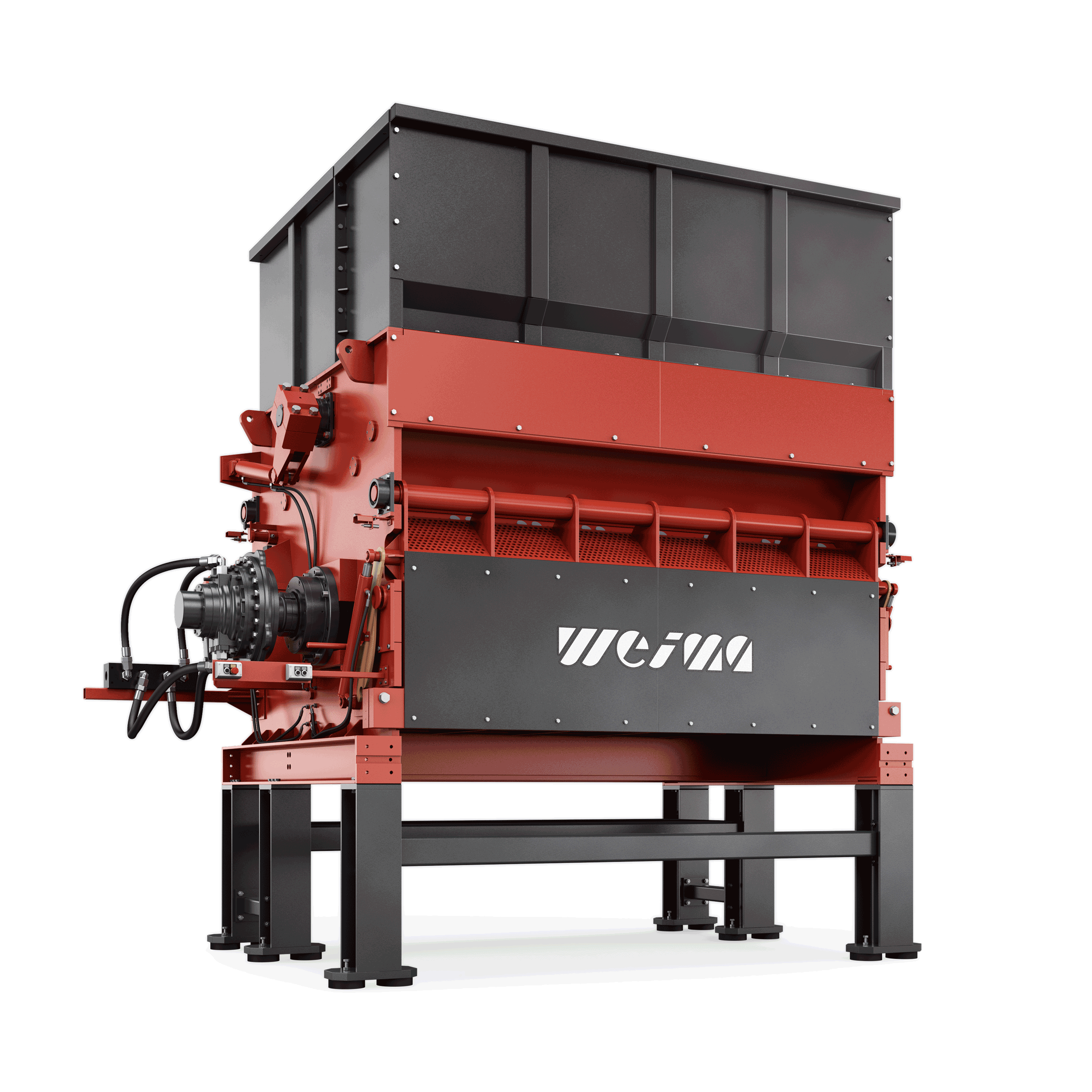
WEIMA PowerLine shredder
Select your preferred drive:
High-Torque drive
The high-torque, multi-pole synchronous motor from Baumüller is produced in Germany and is characterized by its insensitivity to foreign bodies. Without gears, the drive resists shocks and vibrations and thus has a particularly long service life – even when shredding challenging material streams.

Acionamento de alto binário da Baumüller
Hydraulic drive
Hydraulic drives from Hägglunds / Bosch Rexroth have no gearbox and are therefore particularly insensitive to many contaminants. Speed and torque can be adjusted without current peaks. The robust drive provides high torque at low kW power. The speed can be variably adjusted by means of a regulating pump.
Heavy duty machine design
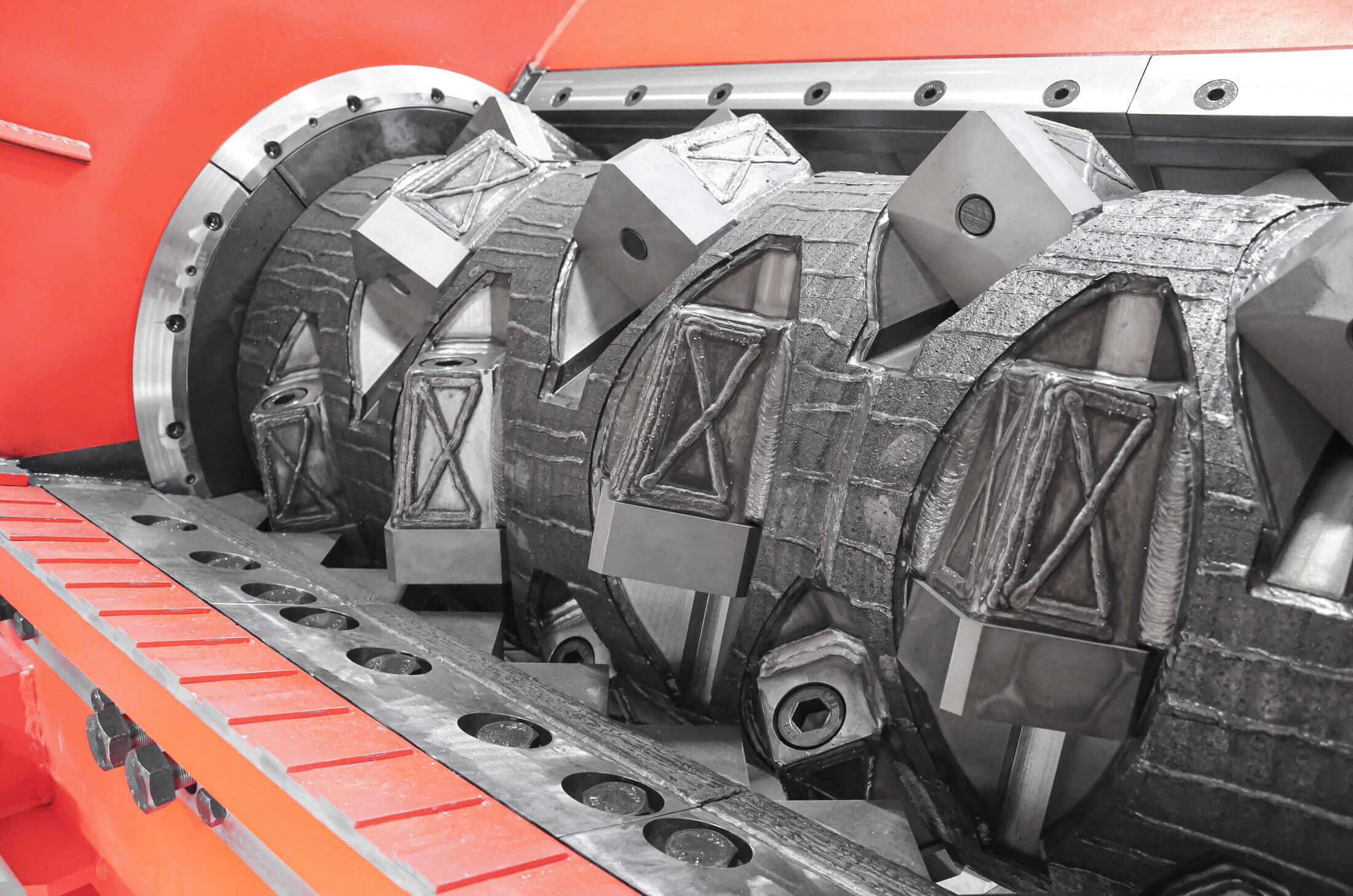
WEIMA shredders for processing highly abrasive materials can be protected with various options to reduce wear and thus downtime and maintenance costs. The heavy wall thickness of the machine frame makes WEIMA shredders particularly robust. The rotor can be reinforced with Vautid, the screen with Creusabro. To protect the cutting knives against the impact of foreign objects, large knives with edge lengths of up to 130 mm x 130 mm can be selected. If the number of knives is small. Vautid can also protect knife holders.
To avoid increased wear of the rotor face plates, we recommend the installation of replaceable Creusabro wear plates on both sides. The cutting chamber can also be reinforced and optionally lined with exchangeable Creusabro plates. Wear protection does not stop at the screen, which defines the material size. For particularly high wear, we offer a screen reinforced with Creusabro with a wall thickness of approx. 20 mm.
What is Creusabro?
Creusabro is a high performance wear resistant steel. Compared to low alloy wear resistant steels, Creusabro has a higher heat resistance. WEIMA uses Creusabro with a hardness of 58 HRC.
What is Vautid?
Vautid is a buildup welding material that can be applied to components as a welding alloy. In WEIMA shredders, Vautid with 62 HRC is applied.
What is Hardox?
Hardox it an abrasion resistant steel and is mainly used as wear plate with a hardness of up to 600 HBW. Depending on the requirements, different degrees of hardness can be applied.
Only at WEIMA
Heavy-duty machine design
for long service life
Large feed hopper
for easy feeding of particularly long pulper plait sections
Easy maintenance
for minimized downtimes
Many drive options
for maximum throughput
Applied know-how
for minimized operating costs
Fast service
for highest customer satisfaction
All from one source:
Machines, conveyor technology, metal detection, support, spare and wear parts for customized solutions
See for yourself
The WEIMA show room is equipped with shredding and briquetting machines of all sizes and technologies. This enables us to simulate your application as realistically as possible. You have the possibility to send us your material or visit us directly in Ilsfeld. From our gallery you have the best view directly into the cutting chamber. So you can observe the shredding process live.
Request an appointment now
Alternatively you can send us material for testing.
Click here for the form.

Pulper rope shredding